The role of integrins in melanoma: a review
- PMID: 32157692
- PMCID: PMC7167356
- DOI: 10.1111/ijd.14850
The role of integrins in melanoma: a review
Abstract
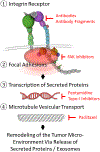
Integrins are the major family of cell adhesion receptors in humans and essential for a wide range of normal physiology, including formation and maintenance of tissue structure integrity, cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation. Integrins also play a prominent role in tumor growth and metastasis. Translational research has tried to define the contribution of integrins to the phenotypic aggressiveness of melanoma because such knowledge is clinically useful. For example, differential expression of integrins in primary cutaneous melanoma can be used to distinguish indolent from aggressive, prometastatic melanoma. Recent studies have shown that gene expression-based testing of patient-derived melanoma tissue is feasible, and molecular tests may fully replace interventional surgical methods such as sentinel lymph node biopsies in the future. Because of their central role in mediating invasion and metastasis, integrins are likely to be useful biomarkers. Integrins are also attractive candidate targets for interventional therapy. This article focuses on the role of integrins in melanoma and highlights recent advances in the field of translational research.
© 2020 the International Society of Dermatology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Hynes RO. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 2002;110(6):673–687. - PubMed
-
- Wegener KL, Partridge AW, Han J, et al. Structural basis of integrin activation by talin. Cell. 2007;128(1):171–182. - PubMed
-
- Winograd-Katz SE, Fässler R, Geiger B, Legate KR. The integrin adhesome: from genes and proteins to human disease. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2014;15(4):273–288. - PubMed
-
- Gu Y, Liu Y, Fu L, et al. Tumor-educated B cells selectively promote breast cancer lymph node metastasis by HSPA4-targeting IgG. Nat Med. 2019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

