Synthesis, Characterization, and Pharmacodynamics Study of Enrofloxacin Mesylate
- PMID: 32158191
- PMCID: PMC7047841
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S239307
Synthesis, Characterization, and Pharmacodynamics Study of Enrofloxacin Mesylate
Abstract
Introduction: Enrofloxacin is used in the treatment of a wide variety of bacterial infections in mammals. However, its poor solubility limits the clinical use.
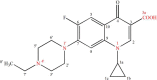
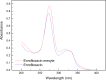
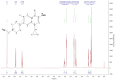
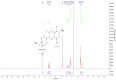
Methods: In order to improve the solubility of enrofloxacin, the enrofloxacin mesylate (EM) were obtained by a chemical synthesis method. The characterization of EM was carried out using ultraviolet scan (UV), synchronous thermal analysis (SDT), fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR) and mass spectrometry (MS), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and X-ray powder diffraction analysis (XRPD). Acute toxicity of EM in Kunming mice was studied. Besides, pharmacokinetic studies were performed in New Zealand rabbits at a single oral dose of 10 mg/kg, and the antibacterial activity of EM was also evaluated.
Results: EM was successfully synthesized and purified. The stoichiometric ratio of mesylate to enrofloxacin was 1:1 and the aqueous solubility of EM was 483.01±4.06 mg/mL, the solubility of EM was about 2000 times higher than enrofloxacin. The oral lethal dose (LD50) of EM was 1168.364 mg/kg, and the pharmacokinetics indicated that the oral relative bioavailability of EM was about 1.79 times and 1.48 times higher than that of enrofloxacin and enrofloxacin hydrochloride, respectively. In addition, the in vitro antibacterial activity of EM was not significantly changed compared with enrofloxacin and enrofloxacin hydrochloride.
Conclusion: EM has higher solubility, low toxicity for oral use, and increases the oral bioavailability in rabbit. This study may be of benefit for the development of new enrofloxacin drugs.
Keywords: acute toxicity; antibacterial effect; characterization; enrofloxacin mesylate; pharmacokinetics.
© 2020 Pei et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Development of an Aqueous Ophthalmic Solution with an Enhanced-Solubility Enrofloxacin Crystal, and its Clinical Evaluation in Dogs.Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(6):726-733. doi: 10.2174/1381612824666180227092606. Curr Pharm Des. 2018. PMID: 29484981
-
Synthesis of new Enrofloxacin Derivatives as Potential Antibiofilm Drugs Against Staphylococcus Aureus and Klebsiella Pneumoniae.Med Chem. 2021;17(1):85-96. doi: 10.2174/1573406416666200402151705. Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32238140
-
Enhancing the solubility and antibacterial activity of novel molecular salts of enrofloxacin drug with isomeric pyridinedicarboxylic acids.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 26;14(1):29317. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80665-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39592802 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of inclusion complex of enrofloxacin with 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin.Drug Deliv. 2020 Dec;27(1):334-343. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2020.1724210. Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 32090640 Free PMC article.
-
Enrofloxacin: pharmacokinetics and metabolism in domestic animal species.Curr Drug Metab. 2013 Dec;14(10):1042-58. doi: 10.2174/1389200214666131118234935. Curr Drug Metab. 2013. PMID: 24261706 Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction of Antibiotics and Humic Substances: Environmental Consequences and Remediation Prospects.Molecules. 2022 Nov 10;27(22):7754. doi: 10.3390/molecules27227754. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36431855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and evaluation of mPEG-PLLA polymeric micelles encapsulating enrofloxacin for enhanced solubility, bioavailability, and antibacterial performance.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Jul 16;12:1595137. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1595137. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40740299 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting therapy effects of composite hyaluronic acid/chitosan nanosystems containing inclusion complexes.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):2734-2741. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2112995. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35983590 Free PMC article.
-
pH-driven entrapment of enrofloxacin in casein-based nanoparticles for the enhancement of oral bioavailability.Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Apr 7;9(8):4057-4067. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2224. eCollection 2021 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34401057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attili AR, Preziuso S, Ngu Ngwa V, et al. Clinical evaluation of the use of enrofloxacin against Staphylococcus aureus clinical mastitis in sheep. Small Ruminant Res. 2016;136:72–77. doi:10.1016/j.smallrumres.2016.01.004 - DOI
-
- Zordok WA, Sadeek SA. Synthesis, thermal analyses, characterization and biological evaluation of new enrofloxacin vanadium(V) solvates(L) (L = An, DMF, Py, Et3N and o-Tol). J Mol Struct. 2016;1120:50–61. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2016.05.011 - DOI
-
- Efthimiadou EK, Karaliota A, Psomas G. Mononuclear metal complexes of the second-generation quinolone antibacterial agent enrofloxacin: synthesis, structure, antibacterial activity and interaction with DNA. Polyhedron. 2008;27(6):1729–1738. doi:10.1016/j.poly.2008.02.006 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

