Second Primary Cancers in Melanoma Patients Critically Shorten Survival
- PMID: 32158273
- PMCID: PMC6986257
- DOI: 10.2147/CLEP.S230149
Second Primary Cancers in Melanoma Patients Critically Shorten Survival
Abstract
Background: Survival in malignant cutaneous melanoma has improved but increasing survival will result in an increased likelihood of the occurrence of second primary cancers (SPCs). SPCs may adversely interfere with survival. We quantified survival in patients with different types of SPCs, in comparison to known poor prognostic indicators of metastatic disease.
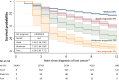
Methods: Data for melanoma and any SPCs were obtained from the Swedish Cancer Registry for years 2003 through 2015, including clinical TNM classification. SPCs were grouped into three 'prognostic groups' based on 5-year relative survival of these cancers as first primary cancer. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were generated and hazard ratios were estimated using Cox regression, adjusted for a number of variables and treating diagnosis of SPC as a time-dependent variable.
Results: The total number of first melanoma patients was 28,716 followed by 3,202 (11.1%) SPCs, 1/3 of which had a second melanoma while 2/3 had other SPCs. Among men diagnosed at age over 70 years, who survived at least 10 years, 31.4% had SPC. HRs (95% CI) for survival increased systematically from the reference rate of 1.00 (no SPC) to 1.59 (1.35-1.87) with SPC of good prognosis (78.6% of SPCs) to 3.49 (2.58-4.72) of moderate prognosis (12.0%) and to 7.93 (5.50-11.44) of poor prognosis (9.4%). In patients without SPC, the HRs increased to 2.62 (2.02-3.39) with any nodal metastases and to 5.88 (4.57-7.57) with any distant metastases compared to patients without local or distant metastases.
Conclusion: The data showed that SPCs are an increasingly common negative prognostic factor for melanoma. Future attempts to improve melanoma survival need to target SPCs.
Keywords: melanoma; metastasis; prognosis; second cancer; survival.
© 2020 Zheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
A.H. is shareholder in Targovax ASA. A.H. is an employee and shareholder in TILT Biotherapeutics Ltd. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Types of second primary cancer influence overall survival in cutaneous melanoma.BMC Cancer. 2021 Oct 19;21(1):1123. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08845-x. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34663263 Free PMC article.
-
Second primary cancers in non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Family history and survival.Int J Cancer. 2020 Feb 15;146(4):970-976. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32391. Epub 2019 May 15. Int J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31054153
-
Impact of family history of cancer on risk and mortality of second cancers in patients with prostate cancer.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2019 Mar;22(1):143-149. doi: 10.1038/s41391-018-0089-y. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2019. PMID: 30185889
-
Incidence of second primary cancers in patients with retinoblastoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 28;14:1372548. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1372548. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38606112 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic factors for early severe pulmonary complications after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2001;7(4):223-9. doi: 10.1053/bbmt.2001.v7.pm11349809. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2001. PMID: 11349809 Review.
Cited by
-
Survival and medical costs of melanoma patients with subsequent cancer diagnoses: A South Korean population-based retrospective cohort study.Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2022 Oct;18(5):e211-e219. doi: 10.1111/ajco.13582. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34166566 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

