Use of Clavien-Dindo Classification System in Assessing Head and Neck Surgery Complications
- PMID: 32158651
- PMCID: PMC7040148
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-019-01718-7
Use of Clavien-Dindo Classification System in Assessing Head and Neck Surgery Complications
Abstract
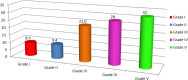
Improving quality of postoperative surgical care in head and neck surgery requires reporting of complications. Clavien-Dindo classification system can be used in grading complications related to head and neck surgery and to assess interobserver variability in grading complex complication scenarios. Data was collected from 242 patients who underwent Head and Neck Surgery from 2015 to 2018 at Dept. of ENT and Head and Neck Surgery at a tertiary care hospital. 177 patients had complications were graded based on Clavien-Dindo classification system, into a 5-scale classification system. Interobserver reliability scores for the complication grading scenarios were found to be statistically significant. Construct validity was confirmed as the length of stay in the hospital was statistically related to complication grade (P = 0.032) Reporting of complications is critical to quality improvement in surgical practice. The Clavien-Dindo complication grading scale system was found to be a useful tool for grading head and neck surgery complications.
Keywords: Clavien classification; Head and neck; Quality improvement; Surgical complications.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Clavien PA, Sanabria JR, Strasberg SM. Proposed classification of complications of surgery with examples of utility in cholecystectomy. Surgery. 1992;111:518–526. - PubMed
-
- Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien P-A. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004;240:205–213. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000133083.54934.ae. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
