Mouse Tumor-Bearing Models as Preclinical Study Platforms for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 32158692
- PMCID: PMC7052016
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00212
Mouse Tumor-Bearing Models as Preclinical Study Platforms for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
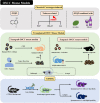
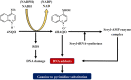
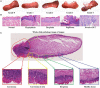
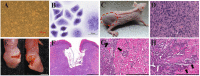
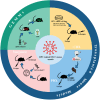
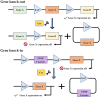
Preclinical animal models of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) have been extensively studied in recent years. Investigating the pathogenesis and potential therapeutic strategies of OSCC is required to further progress in this field, and a suitable research animal model that reflects the intricacies of cancer biology is crucial. Of the animal models established for the study of cancers, mouse tumor-bearing models are among the most popular and widely deployed for their high fertility, low cost, and molecular and physiological similarity to humans, as well as the ease of rearing experimental mice. Currently, the different methods of establishing OSCC mouse models can be divided into three categories: chemical carcinogen-induced, transplanted and genetically engineered mouse models. Each of these methods has unique advantages and limitations, and the appropriate application of these techniques in OSCC research deserves our attention. Therefore, this review comprehensively investigates and summarizes the tumorigenesis mechanisms, characteristics, establishment methods, and current applications of OSCC mouse models in published papers. The objective of this review is to provide foundations and considerations for choosing suitable model establishment methods to study the relevant pathogenesis, early diagnosis, and clinical treatment of OSCC.
Keywords: HPV; OSCC; chemical carcinogen-induced; genetically engineered models; mouse models; syngeneic; transplanted; xenograft.
Copyright © 2020 Li, Dong, Yang, Song, Mou and Ni.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

