Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor of Infancy, a Rapidly Growing Maxillary Alveolar Mass: A Case Report
- PMID: 32158789
- PMCID: PMC7036348
- DOI: 10.30476/DENTJODS.2019.44910
Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor of Infancy, a Rapidly Growing Maxillary Alveolar Mass: A Case Report
Abstract
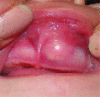
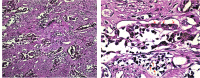
Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy is a rare, rapidly growing, painless, pigmented neoplasm with neural crest derivation. It usually occurs during the first year of life and there is a prominent predilection for the maxilla. The purpose of the present report is to describe additional case of melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy of maxilla in a 6-month-old infant male. The treatment included surgical excision with safe margins. No attempt was made for immediate grafting of the surgery site due to high proliferation rate of tissues and self-renewal during infancy. The facial growth was normal and the surgical cleft was tightly closed. Due to the rarity of tumor, essential knowledge on characteristics of this lesion would contribute to a proper diagnosis and benefit treatment planning.
Keywords: Infant; Neuroectodermal Tumor, Melanotic; Pigmentation; Soft tissue neoplasm.
Copyright: © 2020: Journal of dentistry (Shiraz).
Figures

References
-
- Kruse-Lösler B, Gaertner C, Bürger H, Seper L, Joos U, Kleinheinz J. Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy: systematic review of the literature and presentation of a case. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006; 102: 204–216. - PubMed
-
- Rustagi A, Roychoudhury A, Karak AK. Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy of the maxilla: a case report with review of literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 69: 1120–1124. - PubMed
-
- Rachidi S, Sood AJ, Patel KG, Nguyen SA, Hamilton H, Neville BW, et al. Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor of Infancy: A Systematic Review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015; 73: 1946–1956. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
