Three-dimensional reconstruction of the suborbicularis oculi fat and the infraorbital soft tissue
- PMID: 32158805
- PMCID: PMC7061562
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpra.2018.01.001
Three-dimensional reconstruction of the suborbicularis oculi fat and the infraorbital soft tissue
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding previously published articles.JPRAS Open. 2021 Sep 24;30:172-173. doi: 10.1016/j.jpra.2021.09.006. eCollection 2021 Dec. JPRAS Open. 2021. PMID: 34901366 Free PMC article.
Abstract
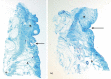
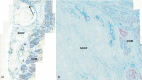
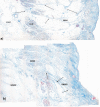
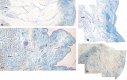
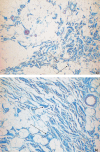
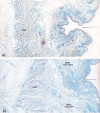
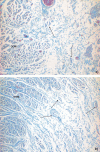
The aim of this study was to reveal the histomorphological connections among the suborbicularis oculi fat (SOOF), the orbicularis oculi muscle (OOM), the superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS), the infraorbital fat and the skin. Full graft tissue blocks of the infraorbital region with the skin, SMAS, OOM and SOOF were collected post mortem from one female and two male formalin-fixed body donors. Serial histological sections were made, stained and digitized. Digitalization and three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of the histological meshwork were performed. SOOF was revealed as a fibro-adipose tissue underlying the OOM, which was strictly separated from the intraorbital fat pad by the orbital septum. SOOF, OOM and SMAS were connected by fibrous septa derived from the SOOF, traversing the OOM with division into multiple muscular bundles, continuing above the muscular plane by forming the SMAS and ending with skin insertion. In the infraorbital region, two different types of SMAS bordering the infraorbital fold have been recognized. Muscle cells have been demonstrated in the SMAS fibrous septa of both SMAS types. Together with the OOM, the SMAS and the skin, SOOF forms an anatomical functional unit. Muscular contraction of the OOM could be transferred by the SMAS to the skin level, producing periorbital mimic expression. The 3D reconstruction facilitates the comprehension of the morphological structure, its connections and space correlations in the infraorbital area. The morphological and topographical peculiarities of the infraorbital structures make it possible to conclude that surgical interventions in this area need to be elaborated and individualized.
Keywords: 3D reconstruction; Infraorbital soft tissue; SMAS; SOOF plastic surgery; Subcutaneous musculoaponeurotic system; Suborbicularis oculi fat.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Figures






Similar articles
-
Facial fold and crease development: A new morphological approach and classification.Clin Anat. 2019 May;32(4):573-584. doi: 10.1002/ca.23355. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Clin Anat. 2019. PMID: 30786074 Free PMC article.
-
Histological, SEM and three-dimensional analysis of the midfacial SMAS - New morphological insights.Ann Anat. 2019 Mar;222:70-78. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2018.11.004. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Ann Anat. 2019. PMID: 30468848
-
Histomorphological analysis of the superficial musculoaponeurotic system in Macaca mulatta species.Ann Anat. 2023 Oct;250:152161. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2023.152161. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Ann Anat. 2023. PMID: 37741583
-
Anatomy of the SMAS revisited.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2003 Jul-Aug;27(4):258-64. doi: 10.1007/s00266-003-3065-3. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2003. PMID: 15058546 Review.
-
Definitions of groove and hollowness of the infraorbital region and clinical treatment using soft-tissue filler.Arch Plast Surg. 2018 May;45(3):214-221. doi: 10.5999/aps.2017.01193. Epub 2018 May 15. Arch Plast Surg. 2018. PMID: 29788683 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
U-SMAS: ultrasound findings of the superficial musculoaponeurotic system.Radiol Bras. 2024 Sep 4;57:e20240035. doi: 10.1590/0100-3984.2024.0035. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Radiol Bras. 2024. PMID: 39268042 Free PMC article.
-
Ectropion Repair Techniques and the Role of Adjunctive Superotemporal Skin Transposition for Tarsal Ectropion.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 27;14(3):827. doi: 10.3390/jcm14030827. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39941498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of the SMAS Flap in Benign Parotid Gland Surgery: Review and 5 Years Experience.J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2025 Apr;24(2):531-535. doi: 10.1007/s12663-024-02207-3. Epub 2024 Jun 6. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2025. PMID: 40182442
-
Facial fold and crease development: A new morphological approach and classification.Clin Anat. 2019 May;32(4):573-584. doi: 10.1002/ca.23355. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Clin Anat. 2019. PMID: 30786074 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aiache A.E., Ramirez O.H. The suborbicularis oculi fat pads: an anatomic and clinical study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1995;95:37–42. - PubMed
-
- Hwang S.H., Hwang K., Jin S., Kim D.J. Location and nature of retro-orbicularis oculus fat and suborbicularis oculi fat. J Craniofac Surg. 2007;18:387–390. - PubMed
-
- Kikkawa D.O., Lemke B.N., Dortzbach R.K. Relations of the superficial musculoaponeurotic system to the orbit and characterization of the orbitomalar ligament. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996;12:77–88. - PubMed
-
- Arnold W.H., Rezwani T., Baric I. Location and distribution of epithelial pearls and tooth buds in human fetuses with cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 1998;35:359–365. - PubMed
-
- Sandulescu T., Spilker L., Rauscher D., Naumova E.A., Arnold W.H. Morphological analysis and three-dimensional reconstruction of the SMAS surrounding the nasolabial fold. Ann Anat. 2018 in review. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

