Treatment of a patient suffering from posttraumatic painful neuromas formed at the bilateral digital nerves of the left middle finger using two neurovascular island flaps
- PMID: 32158846
- PMCID: PMC7061553
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpra.2018.10.001
Treatment of a patient suffering from posttraumatic painful neuromas formed at the bilateral digital nerves of the left middle finger using two neurovascular island flaps
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding previously published articles.JPRAS Open. 2021 Sep 24;30:176-177. doi: 10.1016/j.jpra.2021.09.008. eCollection 2021 Dec. JPRAS Open. 2021. PMID: 34901368 Free PMC article.
Abstract
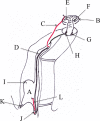
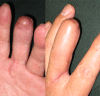
Hand surgeons often encounter painful posttraumatic neuromas in daily practice and the treatment of these neuromas is still challenging for them, because of the tendency of recurrence.1,2 The patient injured his left middle finger and was treated by amputation in a previous hospital. After this operation, the patient started to feel pain at the fingertip and complained of severe electric radiating pain when the radial and ulnar ends of the finger were touched. We treated painful neuromas formed on both palmar digital nerve stumps using a reverse pedicle island flap containing subcutaneous nerves, which were connected to the nerve stumps after removal of the neuromas of the finger. This maneuver relieved the finger pain completely. Removal of finger digital nerve neuromas, connecting the nerve stumps to the subcutaneous nerves included in a skin island flap and, covering the neurorrhaphy sites with the flap may have reduced the chance of the recurrence of neuromas and resulted in restoration of considerable function of the hand.
Keywords: Digit tip amputation; Neurovascular island flap; Painful neuromas; Scar tissue.
© 2018 The Authors.
Figures

References
-
- Herdon JH., Neuromas . Operative hand surgery. 3rd ed. Churchill Livingstone; New York: 1993. In: Green DP, Ed; pp. 1387–1400.
-
- Mackinnon SE, Dellon AL, Hudson AR. Alteration of neuroma formation by manipulation of its microenvironment. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1985;76:345–353. - PubMed
-
- Domeshek LF, Krauss EM, Snyder-Warwick AK. Surgical treatment of neuromas improves patient-reported pain, depression, and quality of life. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;139(2):407–418. - PubMed
-
- Kakinoki R, Ikeguchi R, Atiyya AN. Treatment of posttraumatic painful neuromas at the digit tip using neurovascular island flap. J Hand Surg. 2008;l33A:348–352. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

