Differences in palpebral fissure height depending on patient's intraoperative head position
- PMID: 32158874
- PMCID: PMC7061644
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpra.2019.03.001
Differences in palpebral fissure height depending on patient's intraoperative head position
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding previously published articles.JPRAS Open. 2021 Sep 24;30:176-177. doi: 10.1016/j.jpra.2021.09.008. eCollection 2021 Dec. JPRAS Open. 2021. PMID: 34901368 Free PMC article.
Abstract
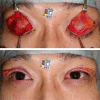
Background: Blepharoptosis operations are performed under local anaesthesia, and it is necessary to determine the location where the levator aponeurosis is fixed to the tarsus by checking opening and closing of the eyelids during surgery. Changes in posture during the operation affect the facial condition in various ways. This study was performed to clarify the differences in palpebral fissure height according to intraoperative head position.
Methods: Sixty subjects (48 women and 12 men aged 20-76 years) were enrolled in the study. The palpebral fissure height of the dominant eye was measured in the head-neutral position and 30° head-down position.
Results: The total fissure height in the 30° head-down position was lower than that in the head-neutral position.
Conclusions: The head-down position affects the patient's fissure height and may mislead the operator. Blepharoptosis operation under local anaesthesia should be performed with the patient in the head-neutral position.
Keywords: Blepharoptosis; Fissure height; Head position; Operation position.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Figures




References
-
- Sultana R., Matsuo K., Yuzuriha S. Disinsertion of the levator aponeurosis from the tarsus in growing children. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000;106(3):563–570. - PubMed
-
- Fujiwara T., Matsuo K., Kondoh S. Etiology and pathogenesis of aponeurotic blepharoptosis. Ann Plast Surg. 2001;46(1):29–35. - PubMed
-
- Ranthbum JE. Entropion. Oculoplastic, Orbital and Reconstructive Surgery vol. I Eyelid. Hornblass A, ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins, 1988:309–324.
-
- Older JJ. Acquired ptosis. Oculoplastic, Orbital and Reconstructive Surgery vol. I Eyelid. Hornblass A, ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins, 1988:341–353.
-
- Matsuo K. Restoration of involuntary tonic contraction of the levator muscle in patients with aponeurotic blepharoptosis or Horner syndrome by aponeurotic advancement using the orbital septum. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. 2003;37(2):81–89. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

