A critical role for plasminogen in inflammation
- PMID: 32159743
- PMCID: PMC7144526
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20191865
A critical role for plasminogen in inflammation
Abstract
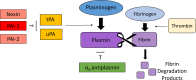
Plasminogen and its active form, plasmin, have diverse functions related to the inflammatory response in mammals. Due to these roles in inflammation, plasminogen has been implicated in the progression of a wide range of diseases with an inflammatory component. In this review, we discuss the functions of plasminogen in inflammatory regulation and how this system plays a role in the pathogenesis of diseases spanning organ systems throughout the body.
© 2020 Baker and Strickland.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Adams R.A., Bauer J., Flick M.J., Sikorski S.L., Nuriel T., Lassmann H., Degen J.L., and Akassoglou K.. 2007. The fibrin-derived gamma377-395 peptide inhibits microglia activation and suppresses relapsing paralysis in central nervous system autoimmune disease. J. Exp. Med. 204:571–582. 10.1084/jem.20061931 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agarwal V., Kuchipudi A., Fulde M., Riesbeck K., Bergmann S., and Blom A.M.. 2013. Streptococcus pneumoniae endopeptidase O (PepO) is a multifunctional plasminogen- and fibronectin-binding protein, facilitating evasion of innate immunity and invasion of host cells. J. Biol. Chem. 288:6849–6863. 10.1074/jbc.M112.405530 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andronicos N.M., Chen E.I., Baik N., Bai H., Parmer C.M., Kiosses W.B., Kamps M.P., Yates J.R. III, Parmer R.J., and Miles L.A.. 2010. Proteomics-based discovery of a novel, structurally unique, and developmentally regulated plasminogen receptor, Plg-RKT, a major regulator of cell surface plasminogen activation. Blood. 115:1319–1330. 10.1182/blood-2008-11-188938 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

