Parity as a Prognostic Factor in Patients with Advanced-Stage Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
- PMID: 32161497
- PMCID: PMC7049748
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S237073
Parity as a Prognostic Factor in Patients with Advanced-Stage Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
Aim: This study aimed to determine the prognostic factors influencing the overall survival (OS) of Iranian women with epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC).
Methods: Information about newly diagnosed patients with confirmed EOC at Motahari Clinic, Shiraz, Iran, from January 1, 2001, to December 31, 2016, was retrospectively reviewed and analyzed. Cox-adjusted proportional hazards (PH) and stratified Cox (SC) models were used to determine the potential prognostic factors.
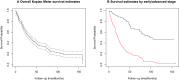
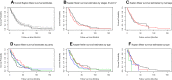
Results: The mean (±SD) age at the diagnosis of 385 patients with EOC was 49.0 (±13.2) years old. Early-stage EOC (ESEOC) and advanced-stage EOC (ASEOC) were diagnosed in 34.3% and 65.7% of the total patients, respectively. The median (95% CI) OS was 35 (28-41) months. For ESEOC patients, a stage II-tumor led to a lower OS in the multivariable analysis compared to a lower stage tumor (P= 0.025). For ASEOC patients, age≥65 years at diagnosis (P=0.008) led to a lower OS. ASEOC patients with 2-5 parities (P=0.014) and >5 parity (P=0.001) demonstrated better OS than nulliparous women.
Conclusion: Patients with ESEOC, higher tumor stage was associated with a shorter OS. The age at diagnosis harmed the OS of patients with ASEOC. More than one parity improved OS in ASEOC patients.
Keywords: advanced-stage epithelial ovarian cancer; early-stage epithelial ovarian cancer; overall survival; parity; stratified Cox-adjusted regression.
© 2020 Khalafi-Nezhad et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

