Tumor-Associated Macrophages: Recent Insights and Therapies
- PMID: 32161718
- PMCID: PMC7052362
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00188
Tumor-Associated Macrophages: Recent Insights and Therapies
Abstract
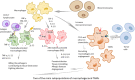
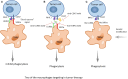
Macrophages, which have functions of engulfing and digesting foreign substances, can clear away harmful matter, including cellular debris and tumor cells. Based on the condition of the internal environment, circulating monocytes give rise to mature macrophages, and when they are recruited into the tumor microenvironment and in suitable conditions, they are converted into tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). Generally, macrophages grow into two main groups called classically activated macrophages (M1) and alternatively activated macrophages (M2). M2 and a small fraction of M1 cells, also known as TAMs, not only lack the function of phagocytizing tumor cells but also help these tumor cells escape from being killed and help them spread to other tissues and organs. In this review, we introduce several mechanisms by which macrophages play a role in the immune regulation of tumor cells, including both killing factors and promoting effects. Furthermore, the targeted therapy for treating tumors based on macrophages is also referred to in our review. We confirm that further studies of macrophage-focused therapeutic strategies and their use in clinical practice are needed to verify their superior efficacy and potential in cancer treatment.
Keywords: immunity; immunity therapy; macrophages; tumor-associated macrophages; tumors.
Copyright © 2020 Zhou, Tang, Gao, Li, Feng and Zhou.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

