CaMeRe: A Novel Tool for Inference of Cancer Metabolic Reprogramming
- PMID: 32161720
- PMCID: PMC7052490
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00207
CaMeRe: A Novel Tool for Inference of Cancer Metabolic Reprogramming
Abstract
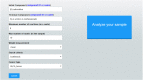
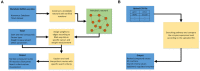
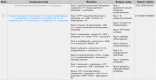
Metabolic reprogramming is prevalent in cancer, largely due to its altered chemical environments such as the distinct intracellular concentrations of O2, H2O2 and H+, compared to those in normal tissue cells. The reprogrammed metabolisms are believed to play essential roles in cancer formation and progression. However, it is highly challenging to elucidate how individual normal metabolisms are altered in a cancer-promoting environment; hence for many metabolisms, our knowledge about how they are changed is limited. We present a novel method, CaMeRe (CAncer MEtabolic REprogramming), for identifying metabolic pathways in cancer tissues. Based on the specified starting and ending compounds, along with gene expression data of given cancer tissue samples, CaMeRe identifies metabolic pathways connecting the two compounds via collection of compatible enzymes, which are most consistent with the provided gene-expression data. In addition, cancer-specific knowledge, such as the expression level of bottleneck enzymes in the pathways, is incorporated into the search process, to enable accurate inference of cancer-specific metabolic pathways. We have applied this tool to predict the altered sugar-energy metabolism in cancer, referred to as the Warburg effect, and found the prediction result is highly accurate by checking the appearance and ranking of those key pathways in the results of CaMeRe. Computational evaluation indicates that the tool is fast and capable of handling large metabolic network inference in cancer tissues. Hence, we believe that CaMeRe offers a powerful tool to cancer researchers for their discovery of reprogrammed metabolisms in cancer. The URL of CaMeRe is http://csbl.bmb.uga.edu/CaMeRe/.
Keywords: cancer; glycosylation; metabolic reprogramming; path-searching; web server.
Copyright © 2020 Li, Zhou, Sun, Qiu, Gao and Xu.
Figures


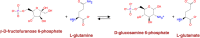


Similar articles
-
Metabolic Reprogramming in Cancer Is Induced to Increase Proton Production.Cancer Res. 2020 Mar 1;80(5):1143-1155. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-3392. Epub 2020 Jan 13. Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 31932456
-
The Warburg effect: essential part of metabolic reprogramming and central contributor to cancer progression.Int J Radiat Biol. 2019 Jul;95(7):912-919. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2019.1589653. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Int J Radiat Biol. 2019. PMID: 30822194 Review.
-
EvoMS: An evolutionary tool to find de novo metabolic pathways.Biosystems. 2015 Aug;134:43-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2015.04.006. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Biosystems. 2015. PMID: 26092635
-
Systematic investigation of metabolic reprogramming in different cancers based on tissue-specific metabolic models.J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2016 Oct;14(5):1644001. doi: 10.1142/S0219720016440017. Epub 2016 Aug 29. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 27760488
-
[Metabolic reprogramming in cancer: the art of balance].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013 Nov;38(11):1177-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7347.2013.11.016. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013. PMID: 24316928 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
The ratio of PKM1/PKM2 is the key factor affecting the glucose metabolism and biological function of colorectal cancer cells.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Jul 31;13(7):3522-3535. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-154. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39145079 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Reprogramming, Questioning, and Implications for Cancer.Biology (Basel). 2021 Feb 7;10(2):129. doi: 10.3390/biology10020129. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33562201 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of MMP-2 and MMP-9 and their associated molecules in the pathogenesis of keloids: a comprehensive review.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 25;15:1444653. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1444653. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39654616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug Repurposing: A Conduit to Unravelling Metabolic Reprogramming for Cancer Treatment.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025;25(8):601-627. doi: 10.2174/0113895575339660250106093738. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39835565 Review.
-
The role of metabolic reprogramming in kidney cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 May 31;14:1402351. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1402351. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38884097 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cazzaniga M, Bonanni B. Relationship between metabolic reprogramming and mitochondrial activity in cancer cells. Understanding the anticancer effect of metformin and its clinical implications. Anticancer Res. (2015) 35:5789–96. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

