The euchromatic histone mark H3K36me3 preserves heterochromatin through sequestration of an acetyltransferase complex in fission yeast
- PMID: 32161768
- PMCID: PMC7052950
- DOI: 10.15698/mic2020.03.711
The euchromatic histone mark H3K36me3 preserves heterochromatin through sequestration of an acetyltransferase complex in fission yeast
Abstract
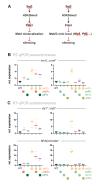
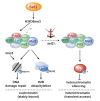
Maintaining the identity of chromatin states requires mechanisms that ensure their structural integrity through the concerted actions of histone modifiers, readers, and erasers. Histone H3K9me and H3K27me are hallmarks of repressed heterochromatin, whereas H3K4me and H3K36me are associated with actively transcribed euchromatin. Paradoxically, several studies have reported that loss of Set2, the methyltransferase responsible for H3K36me, causes de-repression of heterochromatin. Here we show that unconstrained activity of the acetyltransferase complex Mst2C, which antagonizes heterochromatin, is the main cause of the silencing defects observed in Set2-deficient cells. As previously shown, Mst2C is sequestered to actively transcribed chromatin via binding to H3K36me3 that is recognized by the PWWP domain protein Pdp3. We demonstrate that combining deletions of set2 + and pdp3 + results in an epistatic silencing phenotype. In contrast, deleting mst2 + , or other members of Mst2C, fully restores silencing in Set2-deficient cells. Suppression of the silencing defect in set2Δ cells is specific for pericentromeres and subtelomeres, which are marked by H3K9me, but is not seen for loci that lack genuine heterochromatin. Mst2 is known to acetylate histone H3K14 redundantly with the HAT Gnc5. Further, it is involved in the acetylation of the non-histone substrate and E3 ubiquitin ligase Brl1, resulting in increased H2B-K119 ubiquitylation at euchromatin. However, we reveal that none of these mechanisms are responsible for the Set2-dependent silencing pathway, implying that Mst2 targets another, unknown substrate critical for heterochromatin silencing. Our findings demonstrate that maintenance of chromatin states requires spatial constraint of opposing chromatin activities.
Keywords: acetyltransferase; chromatin; heterochromatin; histone modification; silencing.
Copyright: © 2020 Georgescu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Histone Acetyltransferase Mst2 Protects Active Chromatin from Epigenetic Silencing by Acetylating the Ubiquitin Ligase Brl1.Mol Cell. 2017 Jul 20;67(2):294-307.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.05.026. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Mol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28648780 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H3 lysine 36 methylation antagonizes silencing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae independently of the Rpd3S histone deacetylase complex.Genetics. 2007 Feb;175(2):585-93. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.067751. Epub 2006 Dec 18. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17179083 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidation of the Two H3K36me3 Histone Methyltransferases Set2 and Ash1 in Fusarium fujikuroi Unravels Their Different Chromosomal Targets and a Major Impact of Ash1 on Genome Stability.Genetics. 2018 Jan;208(1):153-171. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.1119. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29146582 Free PMC article.
-
The interplay of histone H2B ubiquitination with budding and fission yeast heterochromatin.Curr Genet. 2018 Aug;64(4):799-806. doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0812-1. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 29464330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterochromatin assembly: a new twist on an old model.Chromosome Res. 2006;14(1):83-94. doi: 10.1007/s10577-005-1018-1. Chromosome Res. 2006. PMID: 16506098 Review.
Cited by
-
A systematic quantitative approach comprehensively defines domain-specific functional pathways linked to Schizosaccharomyces pombe heterochromatin regulation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Dec 11;52(22):13665-13689. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39565189 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic quantitative approach comprehensively defines domain-specific functional pathways linked to Schizosaccharomyces pombe heterochromatin regulation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 15:2024.02.13.579970. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.13.579970. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Dec 11;52(22):13665-13689. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1024. PMID: 38405799 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
ISWI chromatin remodeling complexes recruit NSD2 and H3K36me2 in pericentromeric heterochromatin.J Cell Biol. 2024 Aug 5;223(8):e202310084. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202310084. Epub 2024 May 6. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38709169 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional specificity of H3K36 methylation.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2022 May 18;15(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13072-022-00446-7. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2022. PMID: 35581654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subtelomeric Chromatin in the Fission Yeast S. pombe.Microorganisms. 2021 Sep 17;9(9):1977. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9091977. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34576871 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
