RNA profile diversity across arthropoda: guidelines, methodological artifacts, and expected outcomes
- PMID: 32161805
- PMCID: PMC6994094
- DOI: 10.1093/biomethods/bpy012
RNA profile diversity across arthropoda: guidelines, methodological artifacts, and expected outcomes
Abstract
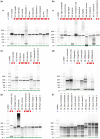
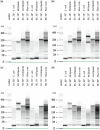
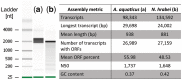
High-quality RNA is an important precursor for high-throughput RNA sequencing (RNAseq) and subsequent analyses. However, the primary metric used to assess RNA quality, the RNA Integrity Number (RIN), was developed based on model bacterial and vertebrate organisms. Though the phenomenon is not widely recognized, invertebrate 28S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is highly prone to a form of denaturation known as gap deletion, in which the subunit collapses into two smaller fragments. In many nonmodel invertebrates, this collapse of the 28S subunit appears as a single band similar in size to the 18S rRNA subunit. This phenomenon is hypothesized to be commonplace among arthropods and is often misinterpreted as a "degraded" rRNA profile. The limited characterization of gap deletion in arthropods, a highly diverse group, as well as other nonmodel invertebrates, often biases RNA quality assessments. To test whether the collapse of 28S is a general pattern or a methodological artifact, we sampled more than half of the major lineages within Arthropoda. We found that the 28S collapse is present in ∼90% of the species sampled. Nevertheless, RNA profiles exhibit considerable diversity with a range of banding patterns. High-throughput RNAseq and subsequent assembly of high-quality transcriptomes from select arthropod species exhibiting collapsed 28S subunits further illustrates the limitations of current RIN proxies in accurately characterizing RNA quality in nonmodel organisms. Furthermore, we show that this form of 28S denaturation, which is often mistaken for true "degradation," can occur at relatively low temperatures.
Keywords: RNAseq; crustaceans; denaturation; gap deletion; genomics; insects; invertebrates; nucleic acids; transcriptomics.
© The Author(s) 2018. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
'Degraded' RNA profiles in Arthropoda and beyond.PeerJ. 2015 Dec 1;3:e1436. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1436. eCollection 2015. PeerJ. 2015. PMID: 26644977 Free PMC article.
-
Fasciola hepatica - where is 28S ribosomal RNA?Exp Parasitol. 2013 Oct;135(2):426-9. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2013.07.026. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Exp Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23954260
-
Insects' RNA Profiling Reveals Absence of "Hidden Break" in 28S Ribosomal RNA Molecule of Onion Thrips, Thrips tabaci.J Nucleic Acids. 2015;2015:965294. doi: 10.1155/2015/965294. Epub 2015 Feb 12. J Nucleic Acids. 2015. PMID: 25767721 Free PMC article.
-
Ecdysozoan phylogeny and Bayesian inference: first use of nearly complete 28S and 18S rRNA gene sequences to classify the arthropods and their kin.Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2004 Apr;31(1):178-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2003.07.013. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2004. PMID: 15019618
-
Molecular characterization of gap region in 28S rRNA molecules in brine shrimp Artemia parthenogenetica and planarian Dugesia japonica.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2012 Apr;77(4):411-7. doi: 10.1134/S000629791204013X. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2012. PMID: 22809161
Cited by
-
De novo transcriptomes of cave and surface isopod crustaceans: insights from 11 species across three suborders.Sci Data. 2024 Jun 6;11(1):595. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03393-y. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 38844536 Free PMC article.
-
Daily transcriptomes of the copepod Calanus finmarchicus during the summer solstice at high Arctic latitudes.Sci Data. 2020 Nov 24;7(1):415. doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-00751-4. Sci Data. 2020. PMID: 33235200 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling of Glycosidases, Lipases, and Proteases from Invasive Asian Palm Weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus.Insects. 2025 Apr 17;16(4):421. doi: 10.3390/insects16040421. Insects. 2025. PMID: 40332944 Free PMC article.
-
Computational discovery of hidden breaks in 28S ribosomal RNAs across eukaryotes and consequences for RNA Integrity Numbers.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 20;9(1):19477. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55573-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31863008 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of RNA extraction protocols from cladocerans.PLoS One. 2022 Apr 26;17(4):e0264989. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264989. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35472091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achim K, Pettit JB, Saraiva LR. et al. High-throughput spatial mapping of single-cell RNA-seq data to tissue of origin. Nat Biotechnol 2015;33:503.. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
