Comparative Evaluation of Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Fibrin and Hank's Balanced Salt Solution as a Storage Medium for Avulsed Teeth: An In Vitro Study
- PMID: 32161897
- PMCID: PMC7006589
- DOI: 10.14744/eej.2019.24633
Comparative Evaluation of Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Fibrin and Hank's Balanced Salt Solution as a Storage Medium for Avulsed Teeth: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
Objective: To compare the efficacy of platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) and Hank's balanced salt solution (HBSS) in the preservation of the periodontal ligament (PDL) cells viability of avulsed teeth.
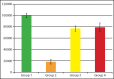
Methods: A total of 30 non-carious third molars with healthy periodontium, indicated for extraction for orthodontic reasons or chronic pericoronitis, were selected for the study. Samples were divided into four groups: one standard group and one experimental group in addition to two control groups (positive and negative). The positive and negative control group corresponded to immediate and 2-hour dry time respectively. The experimental teeth were bench dried for 40 minutes and then immersed in one of the two storage media: HBSS (standard storage media) and PRF (experimental storage media) for 45 minutes. The teeth in each group were treated with dispase II and collagenase for 30 minutes and later centrifuged for 4 minutes at 1000 rpm. The supernatant was removed with sterile micropipette, the cells were labeled with 0.4% trypan blue, and the number of viable PDL cells was counted with a hemocytometer under a light microscope. One-way Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney U test with Boneferroni correction were used for statistical analysis.
Results: Results did not demonstrate any statistically significant differences in the viability of PDL cells between the groups with standard and experimental storage media. Group 1 showed a statistically significant difference of mean compared to Groups 2, 3 and 4. When Group 2 was compared with Groups 3 and 4, a P-value>0.05 suggested no statistical significance.
Conclusion: Within the parameters of this study, HBSS and PRF demonstrated a similar number of viable PDL cells. Hence, PRF could be a used as a good substitute of HBSS as a storage media for avulsed teeth.
Keywords: Avulsion; HBSS; PDL cell viability; platelet-rich fibrin; storage media.
Copyright: © 2019 European Endodontic Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Donaldson M, Kinirons MJ. Factors affecting the time of onset of resorption in avulsed and replanted incisor teeth in children. Dent Traumatol. 2001;17(5):205–9. - PubMed
-
- Hiremath H, Kulkarni S, Sharma R, Hiremath V, Motiwala T. Use of platelet-rich fibrin as an autologous biologic rejuvenating media for avulsed teeth - an in vitro study. Dent Traumatol. 2014;30(6):442–6. - PubMed
-
- Khademi AA, Saei S, Mohajeri MR, Mirkheshti N, Ghassami F, Torabi nia N, et al. A new storage medium for an avulsed tooth. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2008;9(6):25–32. - PubMed
-
- Udoye CI, Jafarzadeh H, Abbott PV. Transport media for avulsed teeth:a review. Aust Endod J. 2012;38(3):129–36. - PubMed
-
- Krasner PR. Avulsed teeth:improving the diagnosis. Dent Prod Rep. 2007;2:l52–64.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources