Radiomics for lung adenocarcinoma manifesting as pure ground-glass nodules: invasive prediction
- PMID: 32162003
- PMCID: PMC7305264
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-020-06776-y
Radiomics for lung adenocarcinoma manifesting as pure ground-glass nodules: invasive prediction
Abstract
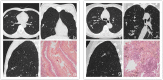
Objectives: To investigate the value of radiomics based on CT imaging in predicting invasive adenocarcinoma manifesting as pure ground-glass nodules (pGGNs).
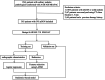
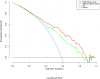
Methods: This study enrolled 395 pGGNs with histopathology-confirmed benign nodules or adenocarcinoma. A total of 396 radiomic features were extracted from each labeled nodule. A Rad-score was constructed with the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) in the training set. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was conducted to establish the radiographic model and the combined radiographic-radiomics model. The predictive performance was validated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Based on the multivariate logistic regression analysis, an individual prediction nomogram was developed and the clinical utility was assessed.
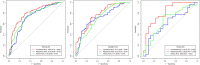
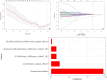
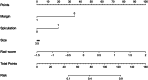
Results: Five radiomic features and four radiographic features were selected for predicting the invasive lesions. The combined radiographic-radiomics model (AUC 0.77; 95% CI, 0.69-0.86) performed better than the radiographic model (AUC 0.71; 95% CI, 0.62-0.81) and Rad-score (AUC 0.72; 95% CI, 0.63-0.81) in the validation set. The clinical utility of the individualized prediction nomogram developed using the Rad-score, margin, spiculation, and size was confirmed in the validation set. The decision curve analysis (DCA) indicated that using a model with Rad-score to predict the invasive lesion would be more beneficial than that without Rad-score and the clinical model.
Conclusions: The proposed radiomics-based nomogram that incorporated the Rad-score, margin, spiculation, and size may be utilized as a noninvasive biomarker for the assessment of invasive prediction in patients with pGGNs.
Key points: • CT-based radiomics analysis helps invasive prediction manifested as pGGNs. • The combined radiographic-radiomics model may be utilized as a noninvasive biomarker for predicting invasive lesion for pGGNs. • Radiomics-based individual nomogram may serve as a vital decision support tool to identify invasive pGGNs, obviating further workup and blind follow-up.
Keywords: Adenocarcinoma; Lung; Nomograms; Solitary pulmonary nodule; X-ray computed tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
One of the authors of this manuscript (Shaofeng Duan) is an employee of GE Healthcare. The remaining authors declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

