Regulation of stanniocalcin-1 secretion by BeWo cells and first trimester human placental tissue from normal pregnancies and those at increased risk of developing preeclampsia
- PMID: 32162740
- PMCID: PMC7318576
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201902426R
Regulation of stanniocalcin-1 secretion by BeWo cells and first trimester human placental tissue from normal pregnancies and those at increased risk of developing preeclampsia
Abstract
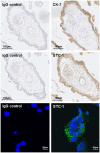
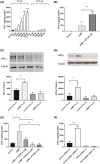
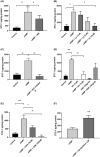
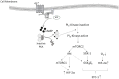
Stanniocalcin-1 (STC-1) is a multi-functional glycosylated peptide present in the plasma of healthy women postpartum and increased further in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. Although the STC-1 gene is expressed by the placenta what regulates its secretion and from which cells at the feto-maternal interface is unknown. Here, we demonstrate for the first time that the syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast are a major site of STC-1 protein expression in first trimester placental tissue. Further, in response to low oxygen, first trimester chorionic villous tissue from pregnancies at increased risk of developing preeclampsia secreted significantly more STC-1 than normal tissue under the same conditions. Using the human trophoblast cell line BeWo we have shown that low oxygen increased the secretion of STC-1 but it required co-stimulation with the Adenosine-3', 5'-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) analogue, 8-Bromo adenosine-3', 5'-cyclic monophosphate cAMP (8 Br-cAMP) to reach significance. Inhibition of Hypoxia inducible factor 2α (HIF-2α) and the Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3 -Kinase)/AKT/Serum and glucocorticoid-induced kinase-1(SGK-1) pathway resulted in significant inhibition of STC-1 secretion. As both low oxygen and cAMP are known to play a central role in placental function, their regulation of STC-1 points to a potentially important role in the maintenance of a normal healthy pregnancy and we would hypothesize that it may act to protect against prolonged placental hypoxia seen in preeclampsia.
Keywords: first trimester; hypoxia; placenta; stanniocalcin-1; trophoblasts.
© 2020 The Authors. The FASEB Journal published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chang AC, Janosi J, Hulsbeek M, et al. A novel human cDNA highly homologous to the fish hormone stanniocalcin. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1995;112:241‐247. - PubMed
-
- Ellard JP, McCudden CR, Tanega C, et al. The respiratory effects of stanniocalcin‐1 (STC‐1) on intact mitochondria and cells: STC‐1 uncouples oxidative phosphorylation and its actions are modulated by nucleotide triphosphates. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007;264:90‐101. - PubMed
-
- Sheikh‐Hamad D, Bick R, Wu GY, et al. Stanniocalcin‐1 is a naturally occurring L‐channel inhibitor in cardiomyocytes: relevance to human heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003;285:H442‐H448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

