Reduction in All-Cause Mortality with Fluticasone Furoate/Umeclidinium/Vilanterol in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 32162970
- PMCID: PMC7301738
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201911-2207OC
Reduction in All-Cause Mortality with Fluticasone Furoate/Umeclidinium/Vilanterol in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
Rationale: The IMPACT (Informing the Pathway of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Treatment) trial demonstrated a significant reduction in all-cause mortality (ACM) risk with fluticasone furoate/umeclidinium/vilanterol (FF/UMEC/VI) versus UMEC/VI in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) at risk of future exacerbations. Five hundred seventy-four patients were censored in the original analysis owing to incomplete vital status information.Objectives: Report ACM and impact of stepping down therapy, following collection of additional vital status data.Methods: Patients were randomized 2:2:1 to FF/UMEC/VI 100/62.5/25 μg, FF/VI 100/25 μg, or UMEC/VI 62.5/25 μg following a run-in on their COPD therapies. Time to ACM was prespecified. Additional vital status data collection and subsequent analyses were performed post hoc.Measurements and Main Results: We report vital status data for 99.6% of the intention-to-treat population (n = 10,355), documenting 98 (2.36%) deaths on FF/UMEC/VI, 109 (2.64%) on FF/VI, and 66 (3.19%) on UMEC/VI. For FF/UMEC/VI, the hazard ratio for death was 0.72 (95% confidence interval, 0.53-0.99; P = 0.042) versus UMEC/VI and 0.89 (95% confidence interval, 0.67-1.16; P = 0.387) versus FF/VI. Independent adjudication confirmed lower rates of cardiovascular and respiratory death and death associated with the patient's COPD.Conclusions: In this secondary analysis of an efficacy outcome from the IMPACT trial, once-daily single-inhaler FF/UMEC/VI triple therapy reduced the risk of ACM versus UMEC/VI in patients with symptomatic COPD and a history of exacerbations.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02164513.
Keywords: COPD; mortality; survival; triple therapy.
Figures

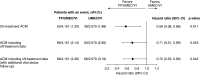

Comment in
-
Fixed Triple Therapy in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Survival. Living Better, Longer, or Both?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Jun 15;201(12):1463-1464. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202003-0622ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32212973 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Mortality in IMPACT: Confounded by Asthma?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Sep 1;202(5):772-773. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202004-1159LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32396735 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to Suissa: Mortality in IMPACT: Confounded by Asthma?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Sep 1;202(5):773-774. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202004-1399LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32396736 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to López-Campos et al.: Triple-Therapy Trials for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Methodological Considerations in the Mortality Effect.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Apr 1;203(7):928-929. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202012-4494LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33444516 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Anthonisen NR, Skeans MA, Wise RA, Manfreda J, Kanner RE, Connett JE Lung Health Study Research Group. The effects of a smoking cessation intervention on 14.5-year mortality: a randomized clinical trial. Ann Intern Med. 2005;142:233–239. - PubMed
-
- Nocturnal Oxygen Therapy Trial Group. Continuous or nocturnal oxygen therapy in hypoxemic chronic obstructive lung disease: a clinical trial. Ann Intern Med. 1980;93:391–398. - PubMed
-
- Medical Research Council Working Party. Long term domiciliary oxygen therapy in chronic hypoxic cor pulmonale complicating chronic bronchitis and emphysema: report of the Medical Research Council Working Party. Lancet. 1981;1:681–686. - PubMed
-
- Fishman A, Martinez F, Naunheim K, Piantadosi S, Wise R, Ries A, et al. National Emphysema Treatment Trial Research Group. A randomized trial comparing lung-volume-reduction surgery with medical therapy for severe emphysema. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2059–2073. - PubMed
-
- Calverley PM, Anderson JA, Celli B, Ferguson GT, Jenkins C, Jones PW, et al. TORCH investigators. Salmeterol and fluticasone propionate and survival in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:775–789. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

