Inflammatory Mechanisms of HCC Development
- PMID: 32164265
- PMCID: PMC7139884
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12030641
Inflammatory Mechanisms of HCC Development
Abstract
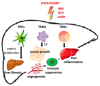
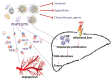
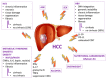
HCC (hepatocellular carcinoma) is the second leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide, with several etiologic causes, mostly inflammation-associated. Different inflammatory responses in the liver can be triggered by different etiological agents. The inflammatory process can be resolved or be persistent, depending on the etiology and multiple other factors. Chronic inflammation, tissue remodeling, genetic alterations, and modifications in cellular signaling are considered to be key processes promoting immunosuppression. The progressive immunosuppression leads to the inactivation of anti-tumor immunity involved in HCC carcinogenesis and progression. Tumor cellular processes including DNA damage, necrosis, and ER (endoplasmic reticulum) stress can affect both immune-surveillance and cancer-promoting inflammation, supporting a mutual interdependence. Here, we review the current understanding of how chronic liver injury and inflammation is triggered and sustained, and how inflammation is linked to HCC. The identification of many hepatic microenvironmental inflammatory processes and their effector molecules, has resulted in extensive translational work and promising clinical trials of new immunomodulatory agents.
Keywords: HCC; cancer etiology; chronic inflammation; immunosuppression; immunosurveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tu T., Budzinska M.A., Maczurek A.E., Cheng R., Di Bartolomeo A., Warner F.J., McCaughan G.W., McLennan S.V., Shackel N.A. Novel aspects of the liver microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis and development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014;15:9422–9458. doi: 10.3390/ijms15069422. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

