Contribution of Cross-Linker and Silica Morphology on Cr(VI) Sorption Performances of Organic Anion Exchangers Embedded into Silica Pores
- PMID: 32164286
- PMCID: PMC7179461
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25051249
Contribution of Cross-Linker and Silica Morphology on Cr(VI) Sorption Performances of Organic Anion Exchangers Embedded into Silica Pores
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Dragan, E.S., et al., Contribution of Cross-Linker and Silica Morphology on Cr(VI) Sorption Performances of Organic Anion Exchangers Embedded into Silica Pores. Molecules 2020, 25, 1249.Molecules. 2020 Jun 12;25(12):2736. doi: 10.3390/molecules25122736. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32545669 Free PMC article.
Abstract
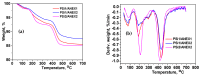
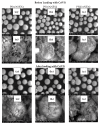
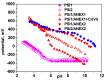
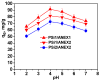
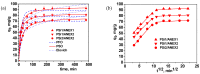
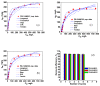
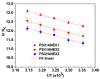
Removal of Cr(VI) from the environment represents a stringent issue because of its tremendous effects on living organisms. In this context, design of sorbents with high sorption capacity for Cr(VI) is getting a strong need. For this purpose, poly(vinylbenzyl chloride), impregnated into porous silica (PSi), was cross-linked with either N,N,N',N'-tetramethyl-1,2-ethylenediamine (TEMED) or N,N,N',N'-tetramethyl-1,3-propanediamine, followed by the reaction of the free -CH2Cl groups with N,N-diethyl-2-hydroxyethylamine to generate strong base anion exchangers (ANEX) inside the pores. The PSi/ANEX composite sorbents were deeply characterized by FTIR spectroscopy, SEM-energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and water uptake. The sorption performances of composites against Cr(VI) were investigated as a function of pH, contact time, initial concentration of Cr(VI), and temperature. It was found that the cross-linker structure and the silica morphology are the key factors controlling the sorption capacity. The adsorption process was spontaneous and endothermic and well described by pseudo-second-order kinetic and Sips isotherm models. The maximum sorption capacity of 311.2 mg Cr(VI)/g sorbent was found for the composite prepared with mesoporous silica using TEMED as cross-linker. The PSi/ANEX composite sorbents represent an excellent alternative for the removal of Cr(VI) oxyanions, being endowed with fast kinetics, equilibrium in about 60 min, and a high level of reusability in successive sorption/desorption cycles.
Keywords: anion exchanger; chromium (VI); cross-linker; porous silica; reusability; sorption isotherm; sorption kinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Owlad M., Aroua M.K., Wan Daud W.A., Baroutian S. Removal of hexavalent chromium-contaminated water and wastewater: A review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009;200:59–77. doi: 10.1007/s11270-008-9893-7. - DOI
-
- Dragan E.S., Avram E., Axente D., Marcu C. Ion-exchange resins. III. Functionalization-morphology correlations in the synthesis of some macroporous, strong basic anion exchangers and uranium-sorption properties evaluation. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2004;42:2451–2461. doi: 10.1002/pola.20106. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

