Cockle Shell-Derived Aragonite CaCO3 Nanoparticles for Co-Delivery of Doxorubicin and Thymoquinone Eliminates Cancer Stem Cells
- PMID: 32164352
- PMCID: PMC7084823
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21051900
Cockle Shell-Derived Aragonite CaCO3 Nanoparticles for Co-Delivery of Doxorubicin and Thymoquinone Eliminates Cancer Stem Cells
Abstract
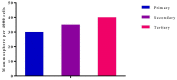
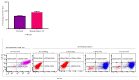
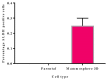
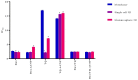
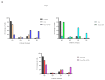
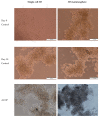
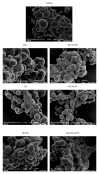
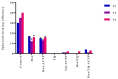
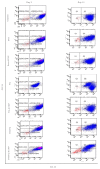
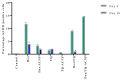
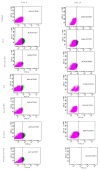
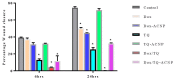
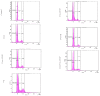
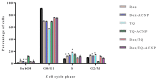
Cancer stem cells CSCs (tumour-initiating cells) are responsible for cancer metastasis and recurrence associated with resistance to conventional chemotherapy. This study generated MBA MD231 3D cancer stem cells enriched spheroids in serum-free conditions and evaluated the influence of combined doxorubicin/thymoquinone-loaded cockle-shell-derived aragonite calcium carbonate nanoparticles. Single loaded drugs and free drugs were also evaluated. WST assay, sphere forming assay, ALDH activity analysis, Surface marker of CD44 and CD24 expression, apoptosis with Annexin V-PI kit, cell cycle analysis, morphological changes using a phase contrast light microscope, scanning electron microscopy, invasion assay and migration assay were carried out; The combination therapy showed enhanced apoptosis, reduction in ALDH activity and expression of CD44 and CD24 surface maker, reduction in cellular migration and invasion, inhibition of 3D sphere formation when compared to the free drugs and the single drug-loaded nanoparticle. Scanning electron microscopy showed poor spheroid formation, cell membrane blebbing, presence of cell shrinkage, distortion in the spheroid architecture; and the results from this study showed that combined drug-loaded cockle-shell-derived aragonite calcium carbonate nanoparticles can efficiently destroy the breast CSCs compared to single drug-loaded nanoparticle and a simple mixture of doxorubicin and thymoquinone.
Keywords: breast cancer; cancer stem cell; doxorubicin; nanoparticle; thymoquinone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures









References
-
- Ginestier C., Liu S., Diebel M.E., Korkaya H., Luo M., Brown M., Wicinski J., Cabaud O., Charafe-Jauffret E., Birnbaum D., et al. CXCR1 blockade selectively targets human breast cancer stem cells in vitro and in xenografts. J. Clin. Investig. 2010;120:485–497. doi: 10.1172/JCI39397. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

