Glioblastoma Multiforme Stem Cell Cycle Arrest by Alkylaminophenol Through the Modulation of EGFR and CSC Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 32164385
- PMCID: PMC7140667
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9030681
Glioblastoma Multiforme Stem Cell Cycle Arrest by Alkylaminophenol Through the Modulation of EGFR and CSC Signaling Pathways
Abstract
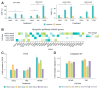
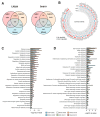
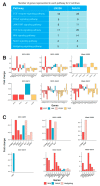
Cancer stem cells (CSCs), a small subpopulation of cells existing in the tumor microenvironment promoting cell proliferation and growth. Targeting the stemness of the CSC population would offer a vital therapeutic opportunity. 3,4-Dihydroquinolin-1(2H)-yl)(p-tolyl)methyl)phenol (THTMP), a small synthetic phenol compound, is proposed to play a significant role in controlling the CSC proliferation and survival. We assessed the potential therapeutic effects of THTMP on glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) and its underlying mechanism in various signaling pathways. To fully comprehend the effect of THTMP on the CSCs, CD133+ GBM stem cell (GSC) and CD133- GBM Non-stem cancer cells (NSCC) population from LN229 and SNB19 cell lines was used. Cell cycle arrest, apoptosis assay and transcriptome analysis were performed for individual cell population. THTMP strongly inhibited NSCC and in a subtle way for GSC in a time-dependent manner and inhibit the resistance variants better than that of temozolomide (TMZ). THTMP arrest the CSC cell population at both G1/S and G2/M phase and induce ROS-mediated apoptosis. Gene expression profiling characterize THTMP as an inhibitor of the p53 signaling pathway causing DNA damage and cell cycle arrest in CSC population. We show that the THTMP majorly affects the EGFR and CSC signaling pathways. Specifically, modulation of key genes involved in Wnt, Notch and Hedgehog, revealed the significant role of THTMP in disrupting the CSCs' stemness and functions. Moreover, THTMP inhibited cell growth, proliferation and metastasis of multiple mesenchymal patient-tissue derived GBM-cell lines. THTMP arrests GBM stem cell cycle through the modulation of EGFR and CSC signaling pathways.
Keywords: GBM stem cells; alkylaminophenol and cell death; cell cycle arrest; non-stem cancer cells; resistance population.
Conflict of interest statement
Supplementary Materials: The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/9/3/681/s1, Table S1: The list shows the genes that were differentially expressed in THTMP vs Untreated in GSC-LN229, Table S2: The list shows the genes that were differentially expressed in THTMP vs Untreated in NSCC-LN229, Table S3: The list shows the genes that were differentially expressed in THTMP vs Untreated in GSC-SNB19, Table S4: The list shows the genes that were differentially expressed in THTMP vs Untreated in NSCC-SNB19, Table S5: The list shows the GO biological processes that were differentially modulated in THTMP vs Untreated in GSC-LN229, Table S6: The list shows the GO biological processes that were differentially modulated in THTMP vs Untreated in NSCC-LN229, Table S7: The list shows the GO biological processes that were differentially modulated in THTMP vs Untreated in GSC-SNB19, Table S8: The list shows the GO biological processes that were differentially modulated in THTMP vs Untreated in NSCC-SNB19, Table S9: The list shows the DEGS that were shared in common with GSC, NSCC and mixed population in LN229, Table S10: The list shows the DEGS that were shared in common with GSC, NSCC and mixed population in SNB19, Figure S1: Growth inhibitory effect of THTMP on different cell lines at 10 μM at 24 h post treatment.
Figures



References
-
- Amarouch A., Mazeron J.J. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant Temozolomide for glioblastoma. Cancer Radiother. 2005;9:196–197.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

