Google trend analysis of climatic zone based Indian severe seasonal sensitive population
- PMID: 32164654
- PMCID: PMC7069044
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-020-8399-0
Google trend analysis of climatic zone based Indian severe seasonal sensitive population
Abstract
Background: Our earlier Google Trend (GT) Analytics study reported that the worldwide human population severely subject to four seasonal (sensitive) comorbid lifestyle diseases (SCLD) such as asthma, obesity, hypertension and fibrosis. The human population subject to seasonal variability in these four diseases activity referred as "severe seasonal sensitive population". In India, the estimated burden of these four seasonal diseases is more than 350 million as on the year 2018. It is a growing crisis for India with a projected disease burden of 500 million in the year 2025. This study was aimed to decipher the genuine SCLD seasonal trends in the entire Indian population using GT and validate these trends in Indian climatic zones.
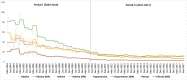
Methods: GT is used to study the temporal trends in web search using weekly Relative Search Volume (RSV) for the period 2004 to 2017. The relative search volume (RSV) of the four-severe seasonal comorbid diseases namely Asthma, Hypertension, Obesity and Fibrosis were collected with and without obesity as the reference. The RSV were collected using the GT selection options as (i) Whole India (ii) Jammu and Kashmir (Cold zone) (iii) Rajasthan (Hot and Dry zone) (iii) West Bengal (Hot and Humid zone) and (iv) Uttar Pradesh state (Composite zone). The time series analysis was carried out to find seasonal patterns, comorbidity, trends and periodicity in the entire India and four of its states (zones).
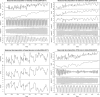
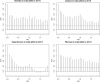
Results: Our analysis of entire India (2004-2017) revealed high significant seasonal patterns and comorbidity in all the four diseases of SCLD. The positive tau values indicated strong positive seasonal trends in the SCLD throughout the period (Table). The auto correlation analysis revealed that these diseases were subjected to 3, 4 and 6 months period seasonal variations. Similar seasonal patterns and trends were also observed in all the four Indian temperature zones. Overall study indicated that SCLD seasonal search patterns and trends are highly conserved in India even in drastic Indian climatic zones.
Conclusions: The clinical outcome arise out of these observations could be of immense significance in handling the major chronic life style diseases asthma, hypertension, obesity and fibrosis. The possible strong comorbid relationship among asthma, hypertension, obesity and fibrosis may be useful to segregate Indian seasonal sensitive population. In disease activity-based chronotherapy, the search interest of segment of the population with access to Internet may be used as an indicator for public health sectors in the early detection of SCLD from a specific country or a region. As this disease population could be highly subject to the adverse effect of seasons in addition to life style and other environmental factors. Our study necessitates that these Indian populations need special attention from the Indian health care sectors.
Keywords: Comorbid; Google trends; Seasonal sensitive population.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Google trend analysis of the Indian population reveals a panel of seasonally sensitive comorbid symptoms with implications for monitoring the seasonally sensitive human population.Popul Health Metr. 2024 Dec 30;22(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12963-024-00349-7. Popul Health Metr. 2024. PMID: 39736745 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic lifestyle diseases display seasonal sensitive comorbid trend in human population evidence from Google Trends.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 12;13(12):e0207359. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207359. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30540756 Free PMC article.
-
Seasonal trends in hypertension in Poland: evidence from Google search engine query data.Kardiol Pol. 2018;76(3):637-641. doi: 10.5603/KP.a2017.0264. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Kardiol Pol. 2018. PMID: 29297185
-
Correlation of regional cardiovascular disease mortality in India with lifestyle and nutritional factors.Int J Cardiol. 2006 Apr 14;108(3):291-300. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2005.05.044. Epub 2005 Jun 22. Int J Cardiol. 2006. PMID: 15978684 Review.
-
More than just a stye: identifying seasonal patterns using google trends, and a review of infodemiological literature in ophthalmology.Orbit. 2023 Apr;42(2):130-137. doi: 10.1080/01676830.2022.2040542. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Orbit. 2023. PMID: 35240907 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Breast Cancer Awareness Month on Public Interest in the United States between 2012 and 2021: A Google Trends Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 21;14(10):2534. doi: 10.3390/cancers14102534. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626141 Free PMC article.
-
Seasonal variation in lifestyle behavior in Poland: Google searches and market sales analysis.BMC Public Health. 2021 Aug 6;21(1):1516. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-11543-9. BMC Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34362345 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the World Inflammatory Bowel Disease Day and Crohn's and Colitis Awareness Week on Population Interest Between 2016 and 2020: Google Trends Analysis.JMIR Infodemiology. 2021 Oct 28;1(1):e32856. doi: 10.2196/32856. eCollection 2021 Jan-Dec. JMIR Infodemiology. 2021. PMID: 37114197 Free PMC article.
-
Google trend analysis of the Indian population reveals a panel of seasonally sensitive comorbid symptoms with implications for monitoring the seasonally sensitive human population.Popul Health Metr. 2024 Dec 30;22(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12963-024-00349-7. Popul Health Metr. 2024. PMID: 39736745 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

