Lipidomic and biophysical homeostasis of mammalian membranes counteracts dietary lipid perturbations to maintain cellular fitness
- PMID: 32165635
- PMCID: PMC7067841
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-15203-1
Lipidomic and biophysical homeostasis of mammalian membranes counteracts dietary lipid perturbations to maintain cellular fitness
Abstract
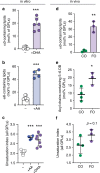
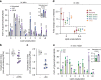
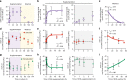
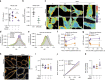
Proper membrane physiology requires maintenance of biophysical properties, which must be buffered from external perturbations. While homeostatic adaptation of membrane fluidity to temperature variation is a ubiquitous feature of ectothermic organisms, such responsive membrane adaptation to external inputs has not been directly observed in mammals. Here, we report that challenging mammalian membranes by dietary lipids leads to robust lipidomic remodeling to preserve membrane physical properties. Specifically, exogenous polyunsaturated fatty acids are rapidly incorporated into membrane lipids, inducing a reduction in membrane packing. These effects are rapidly compensated both in culture and in vivo by lipidome-wide remodeling, most notably upregulation of saturated lipids and cholesterol, resulting in recovery of membrane packing and permeability. Abrogation of this response results in cytotoxicity when membrane homeostasis is challenged by dietary lipids. These results reveal an essential mammalian mechanism for membrane homeostasis wherein lipidome remodeling in response to dietary lipid inputs preserves functional membrane phenotypes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

