Clinical Frailty Scale Score Before ICU Admission Is Associated With Mobility Disability in Septic Patients Receiving Early Rehabilitation
- PMID: 32166247
- PMCID: PMC7063928
- DOI: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000000066
Clinical Frailty Scale Score Before ICU Admission Is Associated With Mobility Disability in Septic Patients Receiving Early Rehabilitation
Abstract
To clarify the relationship between mobility disability at the time of discharge from the ICU and clinical factors evaluated at ICU admission in septic patients.
Design: A single-center, retrospective, observational study.
Setting: Ten-bed, the emergency and medical ICU.
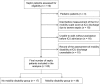
Patients: We analyzed the data of septic patients who were admitted to our ICU between September 2012 and September 2016 and received early rehabilitation.
Interventions: None.
Measurements and main results: The patients were categorized into two groups based on their scores on the ICU mobility scale at the time of discharge from the ICU: the mobility disability group (ICU mobility scale score < 9) and the no mobility disability group (ICU mobility scale score ≥ 9). Of the 110 eligible patients, 63 met the inclusion criteria; of these, 46 patients (73%) were classified into the mobility disability group, and 17 patients (27%) were classified into the no mobility disability group. The age (median, 72 vs 64 yr; p = 0.024), prevalence of patients with clinical frailty scale scores of greater than or equal to 5 (54% vs 12%; p = 0.003), Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score (median, 9.0 vs 6.0; p = 0.006) and rate of vasopressin use (26% vs 0%; p = 0.026) were significantly higher in the mobility disability group as compared with the no mobility disability group. Among the candidate variables for which values recorded before/at the time of ICU admission were available, the clinical frailty scale score was identified as the only independent, statistically significant predictor of mobility disability at ICU discharge (odds ratio, 7.77; 95% CI, 1.37-44.21; p = 0.021). The positive predictive value and negative predictive value of clinical frailty scale scores greater than or equal to 5 for mobility disability at ICU discharge were 92.6% and 41.7%, respectively.
Conclusions: The clinical frailty scale score was associated with increased mobility disability at ICU discharge in septic patients receiving early rehabilitation.
Keywords: clinical frailty scale; early rehabilitation; functional prognosis; intensive care unit mobility scale; mobility disability; sepsis.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have disclosed that they do not have any potential conflicts of interest.
References
-
- Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NK, et al. ; International Forum of Acute Care Trialists Assessment of global incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. Current estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2016193259–272 - PubMed
-
- Kaukonen KM, Bailey M, Suzuki S, et al. Mortality related to severe sepsis and septic shock among critically ill patients in Australia and New Zealand, 2000-2012. JAMA 20143111308–1316 - PubMed
-
- Heyland DK, Hopman W, Coo H, et al. Long-term health-related quality of life in survivors of sepsis. Short form 36: A valid and reliable measure of health-related quality of life. Crit Care Med 2000283599–3605 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous