Graph-Representation of Patient Data: a Systematic Literature Review
- PMID: 32166501
- PMCID: PMC7067737
- DOI: 10.1007/s10916-020-1538-4
Graph-Representation of Patient Data: a Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
Graph theory is a well-established theory with many methods used in mathematics to study graph structures. In the field of medicine, electronic health records (EHR) are commonly used to store and analyze patient data. Consequently, it seems straight-forward to perform research on modeling EHR data as graphs. This systematic literature review aims to investigate the frontiers of the current research in the field of graphs representing and processing patient data. We want to show, which areas of research in this context need further investigation. The databases MEDLINE, Web of Science, IEEE Xplore and ACM digital library were queried by using the search terms health record, graph and related terms. Based on the "Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis" (PRISMA) statement guidelines the articles were screened and evaluated using full-text analysis. Eleven out of 383 articles found in systematic literature review were finally included for analysis in this literature review. Most of them use graphs to represent temporal relations, often representing the connection among laboratory data points. Only two papers report that the graph data were further processed by comparing the patient graphs using similarity measurements. Graphs representing individual patients are hardly used in research context, only eleven papers considered such kind of graphs in their investigations. The potential of graph theoretical algorithms, which are already well established, could help increasing this research field, but currently there are too few papers to estimate how this area of research will develop. Altogether, the use of such patient graphs could be a promising technique to develop decision support systems for diagnosis, medication or therapy of patients using similarity measurements or different kinds of analysis.
Keywords: Electronic health record; Graph theory; Systematic literature review; Temporal patient graph.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
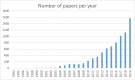
References
-
- Friedman, C., Hripcsak, G., Johnson, S. B. et al. A generalized relational Schema for an integrated clinical patient database. Proc Annu Symp Comput Appl med care: 335–339, 1990
-
- ISO/IEC Information technology—Database languages—SQL—Part 1: Framework (SQL/Framework)(ISO/IEC 9075–1:2016), 2016
-
- Klein J, Gorton I, Ernst N, et al. Performance evaluation of NoSQL databases. In: Singhal R, Chahal D, et al., editors. Proceedings of the 1st workshop on performance analysis of big data systems - PABS ‘15. New York: ACM Press; 2015. pp. 5–10.
-
- Ercan, M. Z., Lane, M., Evaluation of NoSQL databases for EHR systems. In: 25th Australasian conference on information systems, 2014
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

