The orbitofrontal cortex, food intake and obesity
- PMID: 32167268
- PMCID: PMC7850155
- DOI: 10.1503/jpn.190163
The orbitofrontal cortex, food intake and obesity
Abstract
Obesity is a major health challenge facing many people throughout the world. Increased consumption of palatable, high-caloric foods is one of the major drivers of obesity. Both orexigenic and anorexic states have been thoroughly reviewed elsewhere; here, we focus on the cognitive control of feeding in the context of obesity, and how the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) is implicated, based on data from preclinical and clinical research. The OFC is important in decision-making and has been heavily researched in neuropsychiatric illnesses such as addiction and obsessive–compulsive disorder. However, activity in the OFC has only recently been described in research into food intake, obesity and eating disorders. The OFC integrates sensory modalities such as taste, smell and vision, and it has dense reciprocal projections into thalamic, midbrain and striatal regions to fine-tune decision-making. Thus, the OFC may be anatomically and functionally situated to play a critical role in the etiology and maintenance of excess feeding behaviour. We propose that the OFC serves as an integrative hub for orchestrating motivated feeding behaviour and suggest how its neurobiology and functional output might be altered in the obese state.
© 2020 Joule Inc. or its licensors
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
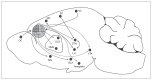
Similar articles
-
Neuroimaging and neuromodulation approaches to study eating behavior and prevent and treat eating disorders and obesity.Neuroimage Clin. 2015 Mar 24;8:1-31. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.03.016. eCollection 2015. Neuroimage Clin. 2015. PMID: 26110109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Executive function in obesity and anorexia nervosa: Opposite ends of a spectrum of disordered feeding behaviour?Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021 Dec 20;111:110395. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2021.110395. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34217755 Review.
-
A Neural Mechanism in the Human Orbitofrontal Cortex for Preferring High-Fat Foods Based on Oral Texture.J Neurosci. 2023 Nov 22;43(47):8000-8017. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1473-23.2023. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37845034 Free PMC article.
-
To eat or not to eat: Effects of food availability on reward system activity during food picture viewing.Appetite. 2016 Apr 1;99:254-261. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2016.01.006. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Appetite. 2016. PMID: 26796027
-
Diet matters: Glucocorticoid-related neuroadaptations associated with calorie intake in female rhesus monkeys.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018 May;91:169-178. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.03.008. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018. PMID: 29567621 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association of Overweight and Obesity with Impaired Executive Functioning in Mexican Adolescents: The Importance of Inhibitory Control.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Jul 9;12(14):1368. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12141368. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39057511 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of orbitofrontal-hypothalamic projections in a murine ALS model and in human patients.Transl Neurodegener. 2021 May 31;10(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s40035-021-00241-6. Transl Neurodegener. 2021. PMID: 34059131 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamical alterations of brain function and gut microbiome in weight loss.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Dec 20;13:1269548. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1269548. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38173792 Free PMC article.
-
Roles for the gut microbiota in regulating neuronal feeding circuits.J Clin Invest. 2021 May 17;131(10):e143772. doi: 10.1172/JCI143772. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 33998595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of 3' Regulatory Region Flanking Kinectin 1 Gene in Schizophrenia.Alpha Psychiatry. 2024 Jun 1;25(3):413-420. doi: 10.5152/alphapsychiatry.2024.241616. eCollection 2024 Jun. Alpha Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39148597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, et al. Prevalence of obesity among adults and youth: United States, 2015–2016. NCHS Data Brief. 2017;288:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, et al. Prevalence of obesity among adults and youth: United States, 2011–2014. NCHS Data Brief. 2015;219:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Apovian CM. Obesity: definition, comorbidities, causes, and burden. Am J Manag Care. 2016;22:s176–85. - PubMed
-
- Finkelstein EA, Ruhm CJ, Kosa KM. Economic causes and consequences of obesity. Annu Rev Public Health. 2005;26:239–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
