Do Massive Allograft Reconstructions for Tumors of the Femur and Tibia Survive 10 or More Years after Implantation?
- PMID: 32168064
- PMCID: PMC7145084
- DOI: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000806
Do Massive Allograft Reconstructions for Tumors of the Femur and Tibia Survive 10 or More Years after Implantation?
Abstract
Background: Massive bone allografts have been used for limb salvage in patients undergoing bone tumor resections as an alternative to endoprostheses. Although several studies on massive allograft reconstructions for bone tumors reported that most complications occur in the first 3 years after surgery, there are no long-term reports on complications to substantiate this contention. We believe such information is important so that surgeons and patients can make more informed decisions when choosing a reconstructive method after tumor resection.
Questions/purposes: (1) What is the survival of allografts free from removal, amputation, or joint replacement in patients treated for bone tumors in the lower limb with a minimum of 10 years of followup? (2) What complications occur after 10 or more years of followup? (3) Are there factors associated with allograft survival, such as age, sex, the affected bone, reconstruction type (intercalary or osteoarticular allograft), tumor type (malignant or benign), failure type, and chemotherapy use?
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the records of 398 patients treated in one center with benign or malignant bone tumors in the femur or tibia between 1986 and 2007. During the period in question, our general indications for using allografts (354 patients) included patients with benign or low-grade sarcomas and patients with high-grade sarcomas with clinical and imaging response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Other approaches such as endoprostheses (44 patients) were indicated if the patient received radiotherapy, in patients with high-grade sarcomas without clinical and imaging response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy, or with neurovascular tumor involvement. We excluded from the analysis 53 patients treated with allograft-prosthetic composites, 46 with hemicondylar osteoarticular allografts, and 57 with intercalary hemicylindrical allografts. The study was thus performed in 198 patients treated with segmental massive allografts in the long bones of the lower extremity (132 femurs and 66 tibias) after resection of a primary bone tumor, including 120 patients treated with osteoarticular and 78 with segmental intercalary allografts. A total of 32 (16%) of the 198 patients died before 10 years, and graft status was known in all of those patients; these patients were included (mean followup, 192 months; range, 1-370 months). All remaining 166 patients who were not known to have died before 10 years were accounted for at least 10 years after the allograft procedure (mean, 222 months; range, 120-370 months). No patient was lost to followup. The mean age was 22 years (range, 2-55 years); 105 patients were male (53%) and 93 were female. The predominant diagnoses were osteosarcoma (n = 125, 63%), giant cell tumor of bone (n = 27, 14%), and Ewing's sarcoma (n = 19, 10%). In all, 146 patients (74%) underwent chemotherapy. Selected variables were analyzed using multivariate logistic regression analyses to identify risk factors of allograft removal, joint replacement, or amputation. We performed competitive risk analysis with allograft removal, joint replacement, or amputation as the endpoint at 5, 10, and 20 years. Patient function was evaluated using the Musculoskeletal Tumor Society (MSTS)-93 scoring system.
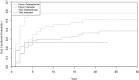
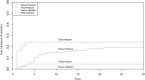
Results: The risk of allograft removal, joint replacement, or amputation was 36% at 5 years (95% CI, 30-43), 40% at 10 years (95% CI, 33-47), and 44% at 20 years (95% CI, 37-51). Fractures occurred in 15% (29 patients), infection in 14% (27 patients), nonunion in 12% (23 patients) and tumor recurrence in 7% (13 patients). Thirty-two patients died of disease before 10 years; nine of these patients had a second surgery before death, eight had an amputation, and one underwent graft removal. Of the 166 patients who were still alive 10 years after the allograft procedure, 36 underwent allograft removal, six patients underwent joint replacement, and four had an amputation; however, after 10 years, six more allografts were removed (four due to fractures, one due to infection, and one due to instability), and another patient was amputated due to a second malignancy. After controlling for potentially confounding variables including death, we found that the risk of allograft removal, joint replacement, or amputation in osteoarticular tibial grafts (58% [95% CI, 43-73] at 5, 10, and 20 years) was higher than that of osteoarticular femur allografts (29% [95% CI, 18-39] at 5 years, 30% [95% CI, 19-40] at 10 years, 37% [95% CI, 25-48] at 20 years; p = 0.010) and tibia intercalary allografts (26% [95% CI, 7-45] at 5, 10 and 20 years; p = 0.020). Fractures occurred more frequently in the femur (18% [95% CI, 11-25]) than in the tibia (5% [95% CI, 0-10]; p < 0.010), and infections occurred more frequently in the tibia (24% [95% CI, 14-35]) than in the femur (4% [95% CI, 0-8]; p < 0.001). With the number of patients we had, we found no difference in the proportion of local recurrence in the tibia (12% [95% CI, 4-20]) compared with the femur (5% [95% CI, 1-9]; p < 0.053).
Conclusions: Infections were the most common complications associated with allograft removal in the first 2 to 3 years after reconstruction and were more frequently associated with tibial allograft removal. Fractures were more commonly associated with graft removal with longer term followup and were more frequently associated with femoral allograft removal. Although we cannot directly compare our results with other types of reconstructions, we believe that allografts still have a role in the reconstruction of patients with a benign or low-grade bone tumor. Future studies in femoral allograft with longer followup should be performed to analyze factors that may explain why some grafts fail, such as the percent of the length of the bone resected, type and number of plates and screws used and type of fixation (rods versus plates). There was a higher incidence of graft removal in patients with proximal tibia osteoarticular allografts, which has led us to use this type of reconstruction only in pediatric patients over the last 15 years.
Level of evidence: Level III, therapeutic study.
Conflict of interest statement
Each author certifies that neither he, nor any member of his immediate family, has funding or commercial associations (consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and
Figures

Comment in
-
CORR Insights®: Do Massive Allograft Reconstructions for Tumors of the Femur and Tibia Survive 10 or More Years After Implantation?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020 Mar;478(3):525-526. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000856. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020. PMID: 31283734 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Aponte-Tinao LA, Ritacco LE, Albergo JI, Ayerza MA, Muscolo DL, Farfalli GL. The principles and applications of fresh frozen allografts to bone and joint reconstruction. Orthop Clin North Am. 2014;45:257-269. - PubMed
-
- Bus MP, Dijkstra PD, van de Sande MA, Taminiau AH, Schreuder HW, Jutte PC, van der Geest IC, Schaap GR, Bramer JA. Intercalary allograft reconstructions following resection of primary bone tumors: a nationwide multicenter study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96:e26. - PubMed
-
- Bus MP, van de Sande MA, Taminiau AH, Dijkstra PD. Is there still a role for osteoarticular allograft reconstruction in musculoskeletal tumour surgery? A long-term follow-up study of 38 patients and systematic review of the literature. Bone Joint J. 2017;99:522-530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

