Oridonin inhibits the migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of small cell lung cancer cells by suppressing FAK-ERK1/2 signalling pathway
- PMID: 32168416
- PMCID: PMC7176879
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.15106
Oridonin inhibits the migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of small cell lung cancer cells by suppressing FAK-ERK1/2 signalling pathway
Abstract
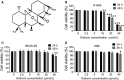
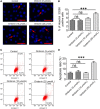
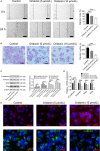
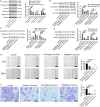
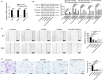
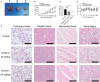
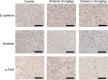
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a severe malignant with high morbidity; however, few effective and secure therapeutic strategy is used in current clinical practice. Oridonin is a small molecule from the traditional Chinese herb Rabdosia rubescens. This study mainly aimed to investigate the role of oridonin on inhibiting the process of H1688, a kind of small cell lung cancer cells from human. Oridonin could suppress H1688 cell proliferation and induce their apoptosis in a high dosage treatment (20 μmol/L). Meanwhile, cell migration was suppressed by oridonin (5 and 10 μmol/L) that did not affect cell proliferation and apoptosis. The expression level of E-cadherin was significantly increased, and the expression of vimentin, snail and slug was reduced after administration of oridonin. These expression changes were associated with the suppressed integrin β1, phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and ERK1/2. In addition, oridonin (5 and 10 mg/kg) inhibited tumour growth in a nude mouse model; however, HE staining revealed a certain degree of cytotoxicity in hepatic tissue after treatment oridonin (10 mg/kg). Furthermore, the concentration of alanine aminotransferase (ALP) was significantly increased and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) was reduced after oridonin treatment (10 mg/kg). Immunohistochemical analysis further revealed that oridonin increased E-cadherin expression and reduced vimentin and phospho-FAK levels in vivo. These findings indicated that oridonin can inhibit the migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of SCLC cells by suppressing the FAK-ERK1/2 signalling pathway. Thus, oridonin may be a new drug candidate to offer an effect of anti-SCLC with relative safety.
Keywords: focal adhesion kinase; migration; oridonin; small cell lung cancer.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oridonin inhibits hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell migration by the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α/matrix metallopeptidase-9 signal pathway in gallbladder cancer.Anticancer Drugs. 2019 Oct;30(9):925-932. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000797. Anticancer Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31517732
-
Oridonin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by negatively regulating AKT/STAT3 signaling pathway.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Jan 1;18(1):81-87. doi: 10.7150/ijms.48552. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33390776 Free PMC article.
-
Oridonin induces apoptosis, inhibits migration and invasion on highly-metastatic human breast cancer cells.Am J Chin Med. 2013;41(1):177-96. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X13500134. Am J Chin Med. 2013. PMID: 23336515
-
Oridonin, a promising antitumor natural product in the chemotherapy of hematological malignancies.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014;15(11):1083-92. doi: 10.2174/1389201015666141111115608. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25391243 Review.
-
The Natural Product Oridonin as an Anticancer Agent: Current Achievements and Problems.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024;25(6):655-664. doi: 10.2174/1389201024666230821110116. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37605407 Review.
Cited by
-
Oridonin from Rabdosia rubescens: An emerging potential in cancer therapy - A comprehensive review.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Feb 1;12(5):3046-3067. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3986. eCollection 2024 May. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38726411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oridonin suppresses gastric cancer SGC-7901 cell proliferation by targeting the TNF-alpha/androgen receptor/TGF-beta signalling pathway axis.J Cell Mol Med. 2023 Sep;27(18):2661-2674. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17841. Epub 2023 Jul 11. J Cell Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37431884 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Epigenetics, Proteomics, and Metabolomics to Reveal the Involvement of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Oridonin-Induced Reproductive Toxicity.Toxics. 2024 May 7;12(5):339. doi: 10.3390/toxics12050339. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 38787118 Free PMC article.
-
An Insight into the Anti-Angiogenic and Anti-Metastatic Effects of Oridonin: Current Knowledge and Future Potential.Molecules. 2021 Feb 3;26(4):775. doi: 10.3390/molecules26040775. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33546106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oridonin inhibited epithelial-mesenchymal transition of laryngeal carcinoma by positively regulating LKB1/AMPK signaling.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Jan 21;21(4):623-632. doi: 10.7150/ijms.92182. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38464825 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:7‐30. - PubMed
-
- Rossi A, Martelli O, Di Maio M. Treatment of patients with small‐cell lung cancer: from meta‐analyses to clinical practice. Cancer Treat Rev. 2013;39:498‐506. - PubMed
-
- Sannino G, Marchetto A, Kirchner T, Grunewald TGP. Epithelial‐to‐Mesenchymal and Mesenchymal‐to‐Epithelial Transition in Mesenchymal Tumors: A Paradox in Sarcomas? Cancer Res. 2017;77:4556‐4561. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

