Electrospun Active Biopapers of Food Waste Derived Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate- co-3-hydroxyvalerate) with Short-Term and Long-Term Antimicrobial Performance
- PMID: 32168913
- PMCID: PMC7153266
- DOI: 10.3390/nano10030506
Electrospun Active Biopapers of Food Waste Derived Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate- co-3-hydroxyvalerate) with Short-Term and Long-Term Antimicrobial Performance
Abstract
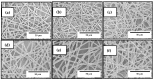
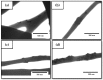
This research reports about the development by electrospinning of fiber-based films made of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) derived from fermented fruit waste, so-called bio-papers, with enhanced antimicrobial performance. To this end, different combinations of oregano essential oil (OEO) and zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) were added to PHBV solutions and electrospun into mats that were, thereafter, converted into homogeneous and continuous films of ~130 μm. The morphology, optical, thermal, mechanical properties, crystallinity, and migration into food simulants of the resultant PHBV-based bio-papers were evaluated and their antimicrobial properties were assessed against Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and Escherichia coli (E. coli) in both open and closed systems. It was observed that the antimicrobial activity decreased after 15 days due to the release of the volatile compounds, whereas the bio-papers filled with ZnONPs showed high antimicrobial activity for up to 48 days. The electrospun PHBV biopapers containing 2.5 wt% OEO + 2.25 wt% ZnONPs successfully provided the most optimal activity for short and long periods against both bacteria.
Keywords: PHBV; active packaging; biopapers; electrospinning; essential oils; inorganic nanoparticles; migration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- Mihindukulasuriya S.D.F., Lim L.T. Nanotechnology development in food packaging: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014;40:149–167. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2014.09.009. - DOI
-
- Singh A.K., Srivastava J.K., Chandel A.K., Sharma L., Mallick N., Singh S.P. Biomedical applications of microbially engineered polyhydroxyalkanoates: An insight into recent advances, bottlenecks, and solutions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019;103:2007–2032. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-09604-y. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bugnicourt E., Cinelli P., Lazzeri A., Alvarez V. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (pha): Review of synthesis, characteristics, processing and potential applications in packaging. Express Polym. Lett. 2014;8:791–808. doi: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2014.82. - DOI
-
- Torres-Giner S., Hilliou L., Melendez-Rodriguez B., Figueroa-Lopez K.J., Madalena D., Cabedo L., Covas J.A., Vicente A.A., Lagaron J.M. Melt processability, characterization, and antibacterial activity of compression-molded green composite sheets made of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) reinforced with coconut fibers impregnated with oregano essential oil. Food Packag. Shelf Life. 2018;17:39–49. doi: 10.1016/j.fpsl.2018.05.002. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

