Sparse Data-Driven Learning for Effective and Efficient Biomedical Image Segmentation
- PMID: 32169002
- PMCID: PMC9351438
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-060418-052147
Sparse Data-Driven Learning for Effective and Efficient Biomedical Image Segmentation
Abstract
Sparsity is a powerful concept to exploit for high-dimensional machine learning and associated representational and computational efficiency. Sparsity is well suited for medical image segmentation. We present a selection of techniques that incorporate sparsity, including strategies based on dictionary learning and deep learning, that are aimed at medical image segmentation and related quantification.
Keywords: dictionary learning; image representation; image segmentation; machine learning; medical image analysis; sparsity.
Figures
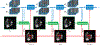



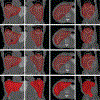
References
-
- Zhang Z, Xu Y, Yang J, Li X, Zhang D. 2015. A survey of sparse representation: algorithms and applications. IEEE Access 3:490–530
-
- Li S, Yin H, Fang L. 2012. Group-sparse representation with dictionary learning for medical image denoising and fusion. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng 59:3450–59 - PubMed
-
- Ma L, Moisan L, Yu J, Zeng T. 2013. A dictionary learning approach for Poisson image deblurring. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 32:1277–89 - PubMed
-
- Onofrey JA, Oksuz I, Sarkar S, Venkataraman R, Staib LH, Papademetris X. 2016. MRI-TRUS image synthesis with application to image-guided prostate intervention. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Simulation and Synthesis in Medical Imaging, pp. 157–66. Berlin: Springer
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

