Comprehensive In Vivo Interrogation Reveals Phenotypic Impact of Human Enhancer Variants
- PMID: 32169219
- PMCID: PMC7179509
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.031
Comprehensive In Vivo Interrogation Reveals Phenotypic Impact of Human Enhancer Variants
Abstract
Establishing causal links between non-coding variants and human phenotypes is an increasing challenge. Here, we introduce a high-throughput mouse reporter assay for assessing the pathogenic potential of human enhancer variants in vivo and examine nearly a thousand variants in an enhancer repeatedly linked to polydactyly. We show that 71% of all rare non-coding variants previously proposed as causal lead to reporter gene expression in a pattern consistent with their pathogenic role. Variants observed to alter enhancer activity were further confirmed to cause polydactyly in knockin mice. We also used combinatorial and single-nucleotide mutagenesis to evaluate the in vivo impact of mutations affecting all positions of the enhancer and identified additional functional substitutions, including potentially pathogenic variants hitherto not observed in humans. Our results uncover the functional consequences of hundreds of mutations in a phenotype-associated enhancer and establish a widely applicable strategy for systematic in vivo evaluation of human enhancer variants.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; Sonic hedgehog; ZRS; cis-regulatory element; enhancer; genome editing; limb development; mutation; polydactyly; rare non-coding variant.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

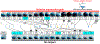


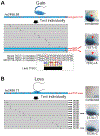
Comment in
-
Deciphering the impact of enhancer variation.Nat Rev Genet. 2020 May;21(5):274-275. doi: 10.1038/s41576-020-0230-3. Nat Rev Genet. 2020. PMID: 32203279 No abstract available.
References
-
- Al-Qattan MM, Abdulkareem, Al I, Haidan, Al Y, and Balwi, Al M. (2012). A novel mutation in the SHHlong-range regulator (ZRS) is associated with preaxial polydactyly, triphalangeal thumb, and severe radial ray deficiency. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 158A, 2610–2615. - PubMed
-
- Albert FW, and Kruglyak L (2015). The role of regulatory variation in complex traits and disease. Nat Rev Genet. - PubMed
-
- Albuisson J, Isidor B, Giraud M, Pichon O, Marsaud T, David A, Le Caignec C, and Bezieau S (2011). Identification of two novel mutations in Shh long-range regulator associated with familial preaxial polydactyly. Clin. Genet. 79, 371–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

