Insulin-like growth factor-1, insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3, and breast cancer risk: observational and Mendelian randomization analyses with ∼430 000 women
- PMID: 32169310
- PMCID: PMC7221341
- DOI: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.01.066
Insulin-like growth factor-1, insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3, and breast cancer risk: observational and Mendelian randomization analyses with ∼430 000 women
Abstract
Background: Epidemiological evidence supports a positive association between circulating insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) concentrations and breast cancer risk, but both the magnitude and causality of this relationship are uncertain. We conducted observational analyses with adjustment for regression dilution bias, and Mendelian randomization (MR) analyses allowed for causal inference.
Patients and methods: We investigated the associations between circulating IGF-1 concentrations and incident breast cancer risk in 206 263 women in the UK Biobank. Multivariable hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were estimated using Cox proportional hazards models. HRs were corrected for regression dilution using repeat IGF-1 measures available in a subsample of 6711 women. For the MR analyses, genetic variants associated with circulating IGF-1 and IGF-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) levels were identified and their association with breast cancer was examined with two-sample MR methods using genome-wide data from 122 977 cases and 105 974 controls.
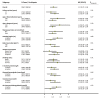
Results: In the UK Biobank, after a median follow-up of 7.1 years, 4360 incident breast cancer cases occurred. In the multivariable-adjusted models corrected for regression dilution, higher IGF-1 concentrations were associated with a greater risk of breast cancer (HR per 5 nmol/l increment of IGF-1 = 1.11, 95% CI = 1.07-1.16). Similar positive associations were found by follow-up time, menopausal status, body mass index, and other risk factors. In the MR analyses, a 5 nmol/l increment in genetically-predicted IGF-1 concentration was associated with a greater breast cancer risk (odds ratio = 1.05, 95% CI = 1.01-1.10; P = 0.02), with a similar effect estimate for estrogen-positive (ER+) tumours, but no effect found for estrogen-negative (ER-) tumours. Genetically-predicted IGFBP-3 concentrations were not associated with breast cancer risk (odds ratio per 1-standard deviation increment = 1.00, 95% CI = 0.97-1.04; P = 0.98).
Conclusion: Our results support a probable causal relationship between circulating IGF-1 concentrations and breast cancer, suggesting that interventions targeting the IGF pathway may be beneficial in preventing breast tumorigenesis.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; breast cancer; insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1); insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3); observational.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pollak M. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:915. - PubMed
-
- Samani A.A., Yakar S., LeRoith D. The role of the IGF system in cancer growth and metastasis: overview and recent insights. Endocr Rev. 2007;28(1):20–47. - PubMed
-
- Kelley K.M., Oh Y., Gargosky S.E. Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins (IGFBPs) and their regulatory dynamics. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1996;28(6):619–637. - PubMed
-
- Perks C.M., Holly J.M.P. IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs) and regulation of breast cancer biology. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008;13(4):455–469. - PubMed
-
- Furlanetto R.W., DiCarlo J.N. Somatomedin-c receptors and growth effects in human breast cells maintained in long-term tissue culture. Cancer Res. 1984;44(5):2122–2128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

