The transcriptional regulator IscR integrates host-derived nitrosative stress and iron starvation in activation of the vvhBA operon in Vibrio vulnificus
- PMID: 32169898
- PMCID: PMC7170529
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.012724
The transcriptional regulator IscR integrates host-derived nitrosative stress and iron starvation in activation of the vvhBA operon in Vibrio vulnificus
Abstract
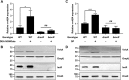
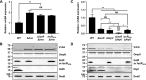
For successful infection of their hosts, pathogenic bacteria recognize host-derived signals that induce the expression of virulence factors in a spatiotemporal manner. The fulminating food-borne pathogen Vibrio vulnificus produces a cytolysin/hemolysin protein encoded by the vvhBA operon, which is a virulence factor preferentially expressed upon exposure to murine blood and macrophages. The Fe-S cluster containing transcriptional regulator IscR activates the vvhBA operon in response to nitrosative stress and iron starvation, during which the cellular IscR protein level increases. Here, electrophoretic mobility shift and DNase I protection assays revealed that IscR directly binds downstream of the vvhBA promoter P vvhBA , which is unusual for a positive regulator. We found that in addition to IscR, the transcriptional regulator HlyU activates vvhBA transcription by directly binding upstream of P vvhBA , whereas the histone-like nucleoid-structuring protein (H-NS) represses vvhBA by extensively binding to both downstream and upstream regions of its promoter. Of note, the binding sites of IscR and HlyU overlapped with those of H-NS. We further substantiated that IscR and HlyU outcompete H-NS for binding to the P vvhBA regulatory region, resulting in the release of H-NS repression and vvhBA induction. We conclude that concurrent antirepression by IscR and HlyU at regions both downstream and upstream of P vvhBA provides V. vulnificus with the means of integrating host-derived signal(s) such as nitrosative stress and iron starvation for precise regulation of vvhBA transcription, thereby enabling successful host infection.
Keywords: H-NS; HlyU; Host-derived signal; IscR; Vibrio vulnificus; bacterial toxin; bacterial transcription; gene regulation; gene transcription; host-pathogen interaction; transcription factor.
© 2020 Choi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures







Similar articles
-
A MARTX Toxin rtxA Gene Is Controlled by Host Environmental Signals through a CRP-Coordinated Regulatory Network in Vibrio vulnificus.mBio. 2020 Jul 28;11(4):e00723-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00723-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32723914 Free PMC article.
-
HlyU acts as an H-NS antirepressor in the regulation of the RTX toxin gene essential for the virulence of the human pathogen Vibrio vulnificus CMCP6.Mol Microbiol. 2009 Apr;72(2):491-505. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06664.x. Epub 2009 Mar 17. Mol Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19320834 Free PMC article.
-
The HlyU protein is a positive regulator of rtxA1, a gene responsible for cytotoxicity and virulence in the human pathogen Vibrio vulnificus.Infect Immun. 2007 Jul;75(7):3282-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00045-07. Epub 2007 Apr 16. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17438022 Free PMC article.
-
The regulator HlyU, the repeat-in-toxin gene rtxA1, and their roles in the pathogenesis of Vibrio vulnificus infections.Microbiologyopen. 2012 Dec;1(4):502-13. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.48. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Microbiologyopen. 2012. PMID: 23233275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatiotemporal Regulation of Vibrio Exotoxins by HlyU and Other Transcriptional Regulators.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Aug 22;12(9):544. doi: 10.3390/toxins12090544. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32842612 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Increased intracellular persulfide levels attenuate HlyU-mediated hemolysin transcriptional activation in Vibrio cholerae.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 13:2023.03.13.532278. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.13.532278. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Biol Chem. 2023 Sep;299(9):105147. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105147. PMID: 36993174 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
IscR-tmRNA regulatory axis plays a key role in multiple stress response and pathogenicity in Aeromonas veronii.Virulence. 2025 Dec;16(1):2530659. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2025.2530659. Epub 2025 Jul 15. Virulence. 2025. PMID: 40665627 Free PMC article.
-
MARTX toxin of Vibrio vulnificus induces RBC phosphatidylserine exposure that can contribute to thrombosis.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 17;13(1):4846. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32599-0. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35978022 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Approaches for Assembling Iron-Sulfur Proteins.mBio. 2021 Dec 21;12(6):e0242521. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02425-21. Epub 2021 Nov 16. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34781750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repression by the H-NS/YmoA histone-like protein complex enables IscR dependent regulation of the Yersinia T3SS.PLoS Genet. 2022 Jul 28;18(7):e1010321. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010321. eCollection 2022 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 35901167 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

