A key mammalian cholesterol synthesis enzyme, squalene monooxygenase, is allosterically stabilized by its substrate
- PMID: 32170014
- PMCID: PMC7132291
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1915923117
A key mammalian cholesterol synthesis enzyme, squalene monooxygenase, is allosterically stabilized by its substrate
Abstract
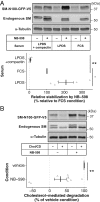
Cholesterol biosynthesis is a high-cost process and, therefore, tightly regulated by both transcriptional and posttranslational negative feedback mechanisms in response to the level of cellular cholesterol. Squalene monooxygenase (SM, also known as squalene epoxidase or SQLE) is a rate-limiting enzyme in the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway and catalyzes epoxidation of squalene. The stability of SM is negatively regulated by cholesterol via its N-terminal regulatory domain (SM-N100). In this study, using a SM-luciferase fusion reporter cell line, we performed a chemical genetics screen that identified inhibitors of SM itself as up-regulators of SM. This effect was mediated through the SM-N100 region, competed with cholesterol-accelerated degradation, and required the E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCH6. However, up-regulation was not observed with statins, well-established cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors, and this pointed to the presence of another mechanism other than reduced cholesterol synthesis. Further analyses revealed that squalene accumulation upon treatment with the SM inhibitor was responsible for the up-regulatory effect. Using photoaffinity labeling, we demonstrated that squalene directly bound to the N100 region, thereby reducing interaction with and ubiquitination by MARCH6. Our findings suggest that SM senses squalene via its N100 domain to increase its metabolic capacity, highlighting squalene as a feedforward factor for the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway.
Keywords: chemical genetics; cholesterol homeostasis; squalene; squalene monooxygenase.
Copyright © 2020 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures






Comment in
-
Squalene and cholesterol in the balance at the ER membrane.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Apr 14;117(15):8228-8230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2003388117. Epub 2020 Apr 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32238557 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Valosin-containing protein mediates the ERAD of squalene monooxygenase and its cholesterol-responsive degron.Biochem J. 2019 Sep 20;476(18):2545-2560. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20190418. Biochem J. 2019. PMID: 31471528
-
Non-canonical ubiquitination of the cholesterol-regulated degron of squalene monooxygenase.J Biol Chem. 2019 May 17;294(20):8134-8147. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007798. Epub 2019 Apr 2. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30940729 Free PMC article.
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCH6 degrades squalene monooxygenase and affects 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl coenzyme A reductase and the cholesterol synthesis pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Apr;34(7):1262-70. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01140-13. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24449766 Free PMC article.
-
Squalene monooxygenase: a journey to the heart of cholesterol synthesis.Prog Lipid Res. 2020 Jul;79:101033. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2020.101033. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Prog Lipid Res. 2020. PMID: 32360125 Review.
-
The shape of human squalene epoxidase expands the arsenal against cancer.Nat Commun. 2019 Feb 21;10(1):888. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08866-y. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30792392 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The mammalian cholesterol synthesis enzyme squalene monooxygenase is proteasomally truncated to a constitutively active form.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100731. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100731. Epub 2021 Apr 30. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33933449 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Cholesterol and Lipid Rafts in Cancer Signaling: A Promising Therapeutic Opportunity?Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 19;9:622908. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.622908. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33816471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High SQLE Expression and Gene Amplification Correlates with Poor Prognosis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Jun 14;13:4709-4723. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S305719. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34163246 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthetic pathways of triterpenoids and strategies to improve their Biosynthetic Efficiency.Plant Growth Regul. 2022;97(3):439-454. doi: 10.1007/s10725-022-00818-9. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Plant Growth Regul. 2022. PMID: 35382096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The contribution of mitochondria-associated ER membranes to cholesterol homeostasis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 11:2024.11.11.622945. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.11.622945. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39605513 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Gil G., Faust J. R., Chin D. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Membrane-bound domain of HMG CoA reductase is required for sterol-enhanced degradation of the enzyme. Cell 41, 249–258 (1985). - PubMed
-
- Sever N., Yang T., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., DeBose-Boyd R. A., Accelerated degradation of HMG CoA reductase mediated by binding of insig-1 to its sterol-sensing domain. Mol. Cell 11, 25–33 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Gill S., Stevenson J., Kristiana I., Brown A. J., Cholesterol-dependent degradation of squalene monooxygenase, a control point in cholesterol synthesis beyond HMG-CoA reductase. Cell Metab. 13, 260–273 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

