Paradoxical activation of the protein kinase-transcription factor ERK5 by ERK5 kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 32170057
- PMCID: PMC7069993
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-15031-3
Paradoxical activation of the protein kinase-transcription factor ERK5 by ERK5 kinase inhibitors
Abstract
The dual protein kinase-transcription factor, ERK5, is an emerging drug target in cancer and inflammation, and small-molecule ERK5 kinase inhibitors have been developed. However, selective ERK5 kinase inhibitors fail to recapitulate ERK5 genetic ablation phenotypes, suggesting kinase-independent functions for ERK5. Here we show that ERK5 kinase inhibitors cause paradoxical activation of ERK5 transcriptional activity mediated through its unique C-terminal transcriptional activation domain (TAD). Using the ERK5 kinase inhibitor, Compound 26 (ERK5-IN-1), as a paradigm, we have developed kinase-active, drug-resistant mutants of ERK5. With these mutants, we show that induction of ERK5 transcriptional activity requires direct binding of the inhibitor to the kinase domain. This in turn promotes conformational changes in the kinase domain that result in nuclear translocation of ERK5 and stimulation of gene transcription. This shows that both the ERK5 kinase and TAD must be considered when assessing the role of ERK5 and the effectiveness of anti-ERK5 therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
N.S.G. is a founder, science advisory board member (SAB) and equity holder in Gatekeeper, Syros, Petra, C4 and Soltego. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
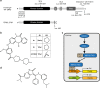

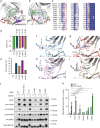
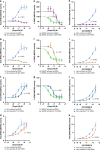
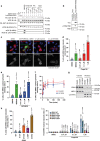

References
-
- Johnson, G. L. ERK1/ERK2 MAPK pathway. (Connections Map in the Database of Cell Signaling, as seen 27 February 2014), http://stke.sciencemag.org/cgi/cm/stkecm;CMP_10705. Sci. Signal. (2005).
-
- Johnson, G. L. JNK MAPK Pathway. (Connections Map in the Database of Cell Signaling, as seen 27 February 2014) http://stke.sciencemag.org/cgi/cm/stkecm;CMP_10827. Sci. Signal. (2003).
-
- Johnson, G. L. p38 MAPK Pathway. (Connections Map in the Database of Cell Signaling, as seen 27 February 2014), http://stke.sciencemag.org/cgi/cm/stkecm;CMP_10958. Sci. Signal.(2008).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 21421/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- MR/K007580/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/N015886/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/J004456/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- A21421/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

