An engineered oncolytic virus expressing PD-L1 inhibitors activates tumor neoantigen-specific T cell responses
- PMID: 32170083
- PMCID: PMC7070065
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-15229-5
An engineered oncolytic virus expressing PD-L1 inhibitors activates tumor neoantigen-specific T cell responses
Abstract
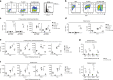
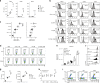
Oncolytic viruses offer an in situ vaccination approach to activate tumor-specific T cell responses. However, the upregulation of PD-L1 expression on tumor cells and immune cells leads to tumor resistance to oncolytic immunotherapy. In this study, we generate an engineered oncolytic virus that coexpresses a PD-L1 inhibitor and GM-CSF. We find that the oncolytic virus is able to secrete the PD-L1 inhibitor that systemically binds and inhibits PD-L1 on tumor cells and immune cells. Importantly, the intratumoral injection with the oncolytic virus overcomes PD-L1-mediated immunosuppression during both the priming and effector phases, provokes systemic T cell responses against dominant and subdominant neoantigen epitopes derived from mutations, and leads to an effective rejection of both virus-injected and distant tumors. In summary, this engineered oncolytic virus is able to activate tumor neoantigen-specific T cell responses, providing a potent, individual tumor-specific oncolytic immunotherapy for cancer patients, especially those resistant to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
X.F.H. and J.C. are employees and shareholders of Pomona Biotechnology Corp. X.F.H. is also a shareholder of LifeSeq Limited Corp. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

