Purinergic signaling and tumor microenvironment in cervical Cancer
- PMID: 32170538
- PMCID: PMC7166227
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-020-09693-3
Purinergic signaling and tumor microenvironment in cervical Cancer
Abstract
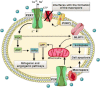
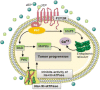
Cervical cancer is the fourth most common type of cancer incidence in the world female population, and it has become a public health problem worldwide. Several factors are involved in this type of cancer, including intrinsic factors related to the inflammatory process, such as extracellular nucleotides and adenosine-components of the purinergic system. The present review focuses on the role of the purinergic system in cervical cancer, especially regarding the interaction of extracellular nucleotides with their respective receptors expressed in the tumor microenvironment of cervical cancer and their role in the host immune response. The high concentrations of extracellular nucleotides in the tumor microenvironment of cervical cancer interfere in the regulation, proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis of cancer cells of the uterine cervix through different P1 and P2 receptor subtypes. Such diverse cellular processes that are mediated by adenosine triphosphate and adenosine across the tumor microenvironment and that also have effects on host immune defense will be reviewed here in detail.
Keywords: Cervical cancer; Ectonucleotidases; Human papillomavirus; Purinergic receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
MS Pfaffenzeller declares that she has no conflict of interest. MLM Franciosi declares that she has no conflict of interest. AM Cardoso declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Campion M, Canfell K. Gynecologic oncology. 6. Filadélfia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015. Cervical Cancer screening and Preinvasive disease; pp. 242–325.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

