Venetoclax in combination with cytarabine with or without idarubicin in children with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukaemia: a phase 1, dose-escalation study
- PMID: 32171069
- PMCID: PMC7153631
- DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30060-7
Venetoclax in combination with cytarabine with or without idarubicin in children with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukaemia: a phase 1, dose-escalation study
Abstract
Background: Outcomes for children with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukaemia remain poor. The BCL-2 inhibitor, venetoclax, has shown promising activity in combination with hypomethylating agents and low-dose cytarabine in older adults for whom chemotherapy is not suitable with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukaemia. We aimed to determine the safety and explore the activity of venetoclax in combination with standard and high-dose chemotherapy in paediatric patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukaemia.
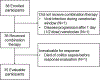
Methods: We did a phase 1, dose-escalation study at three research hospitals in the USA. Eligible patients were aged 2-22 years with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukaemia or acute leukaemia of ambiguous lineage with adequate organ function and performance status. During dose escalation, participants received venetoclax orally once per day in continuous 28-day cycles at either 240 mg/m2 or 360 mg/m2, in combination with cytarabine received intravenously every 12 h at either 100 mg/m2 for 20 doses or 1000 mg/m2 for eight doses, with or without intravenous idarubicin (12 mg/m2) as a single dose, using a rolling-6 accrual strategy. The primary endpoint was the recommended phase 2 dose of venetoclax plus chemotherapy and the secondary endpoint was the proportion of patients treated at the recommended phase 2 dose who achieved complete remission or complete remission with incomplete haematological recovery. Analyses were done on patients who received combination therapy. The study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03194932) and is now enrolling to address secondary and exploratory objectives.
Findings: Between July 1, 2017, and July 2, 2019, 38 patients were enrolled (aged 3-22 years; median 10 [IQR 7-13]), 36 of whom received combination therapy with dose escalation, with a median follow-up of 7·1 months (IQR 5·1-11·2). The recommended phase 2 dose of venetoclax was found to be 360 mg/m2 (maximum 600 mg) combined with cytarabine (1000 mg/m2 per dose for eight doses), with or without idarubicin (12 mg/m2 as a single dose). Overall responses were observed in 24 (69%) of the 35 patients who were evaluable after cycle 1. Among the 20 patients treated at the recommended phase 2 dose, 14 (70%, 95% CI 46-88) showed complete response with or without complete haematological recovery, and two (10%) showed partial response. The most common grade 3-4 adverse events were febrile neutropenia (22 [66%]), bloodstream infections (six [16%]), and invasive fungal infections (six [16%]). Treatment-related death occurred in one patient due to colitis and sepsis.
Interpretation: The safety and activity of venetoclax plus chemotherapy in paediatric patients with heavily relapsed and refractory acute myeloid leukaemia suggests that this combination should be tested in newly diagnosed paediatric patients with high-risk acute myeloid leukaemia.
Funding: US National Institutes of Health, American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities, AbbVie, and Gateway for Cancer Research.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
SYK and TP are employed by AbbVie. Inc. AHS is employed by AbbVie and own stocks. JTO and JER received research funding from AbbVie, Inc and from Gateway for Cancer Research during the conduct of the study. JTO received additional funding from AbbVie outside the submitted work. TBA received travel funds from AbbVie. SEK, AB, SBP, KC, LW, JW, JMK, PEM, SDG, NJL, and CHP declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Venetoclax for paediatric acute myeloid leukaemia: a step forward.Lancet Oncol. 2020 Apr;21(4):476-478. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30136-4. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Lancet Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32171068 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gamis AS, Alonzo TA, Meshinchi S, Sung L, Gerbing RB, Raimondi SC, et al. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin in children and adolescents with de novo acute myeloid leukemia improves event-free survival by reducing relapse risk: results from the randomized phase III Children’s Oncology Group trial AAML0531. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(27):3021–32. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Konopleva M, Zhao S, Hu W, Jiang S, Snell V, Weidner D, et al. The anti-apoptotic genes Bcl-X(L) and Bcl-2 are over-expressed and contribute to chemoresistance of non-proliferating leukaemic CD34+ cells. Br J Haematol. 2002;118(2):521–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

