Clinical characteristics of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 reactivation
- PMID: 32171867
- PMCID: PMC7102560
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.001
Clinical characteristics of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 reactivation
Abstract
Objectives: Previous studies on the pneumonia outbreak caused by the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) were based on information from the general population. However, limited data was available for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) reactivation. This study aimed to evaluate the clinical characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 reactivation.
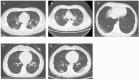
Methods: Clinical records, laboratory results, and chest CT scans were retrospectively reviewed for 55 patients with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 pneumonia (i.e., with throat swab samples that were positive for SARS-CoV-2) who were admitted to Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, from Jan. 8 to Feb. 10, 2020.
Results: All 55 patients had a history of epidemiological exposure to COVID-19, and 5 (9%) patients who discharged from hospital presented with SARS-CoV-2 reactivation. Among the 5 reactivated patients, other symptoms were also observed, including fever, cough, sore throat, and fatigue. One of the 5 patients had progressive lymphopenia (from 1.3 to 0.56 × 109 cells per L) and progressive neutrophilia (from 4.5 to 18.28 × 109 cells per L). All 5 reactivated patients presented normal aminotransferase levels. Throat swab samples from the 5 reactivated patients were tested for SARS-CoV-2, indicating all positive for the virus.
Conclusions: Findings from this small group of cases suggested that there was currently evidence for reactivation of SARS-CoV-2 and there might be no specific clinical characteristics to distinguish them.
Keywords: COVID-19; CT scan; Laboratory medicine; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None.
Comment in
-
Duration for carrying SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 patients.J Infect. 2020 Jul;81(1):e78-e79. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.053. Epub 2020 Apr 10. J Infect. 2020. PMID: 32283161 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Recurrence of COVID-19 after recovery: a case report from Italy.Infection. 2020 Dec;48(6):965-967. doi: 10.1007/s15010-020-01444-1. Epub 2020 May 16. Infection. 2020. PMID: 32415334 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
COVID-19: Outcomes of patients with confirmed COVID-19 re-admitted to hospital.J Infect. 2020 Sep;81(3):e18-e19. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.07.007. Epub 2020 Jul 8. J Infect. 2020. PMID: 32652166 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous