S1P and plasmalogen derived fatty aldehydes in cellular signaling and functions
- PMID: 32171908
- PMCID: PMC7214093
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158681
S1P and plasmalogen derived fatty aldehydes in cellular signaling and functions
Abstract
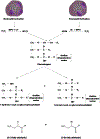
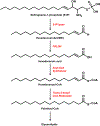
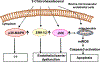
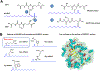
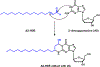
Long-chain fatty aldehydes are present in low concentrations in mammalian cells and serve as intermediates in the interconversion between fatty acids and fatty alcohols. The long-chain fatty aldehydes are generated by enzymatic hydrolysis of 1-alkyl-, and 1-alkenyl-glycerophospholipids by alkylglycerol monooxygenase, plasmalogenase or lysoplasmalogenase while hydrolysis of sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) by S1P lyase generates trans ∆2-hexadecenal (∆2-HDE). Additionally, 2-chloro-, and 2-bromo- fatty aldehydes are produced from plasmalogens or lysoplasmalogens by hypochlorous, and hypobromous acid generated by activated neutrophils and eosinophils, respectively while 2-iodofatty aldehydes are produced by excess iodine in thyroid glands. The 2-halofatty aldehydes and ∆2-HDE activated JNK signaling, BAX, cytoskeletal reorganization and apoptosis in mammalian cells. Further, 2-chloro- and 2-bromo-fatty aldehydes formed GSH and protein adducts while ∆2-HDE formed adducts with GSH, deoxyguanosine in DNA and proteins such as HDAC1 in vitro. ∆2-HDE also modulated HDAC activity and stimulated H3 and H4 histone acetylation in vitro with lung epithelial cell nuclear preparations. The α-halo fatty aldehydes elicited endothelial dysfunction, cellular toxicity and tissue damage. Taken together, these investigations suggest a new role for long-chain fatty aldehydes as signaling lipids, ability to form adducts with GSH, proteins such as HDACs and regulate cellular functions.
Keywords: Hexadecenal; Long-chain fatty aldehydes; Lysoplasmalogenase; Plasmalogenase; S1P; S1P Lyase.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflict of interest and no financial obligations.
Figures
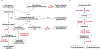





Similar articles
-
Nuclear Sphingosine-1-phosphate Lyase Generated ∆2-hexadecenal is A Regulator of HDAC Activity and Chromatin Remodeling in Lung Epithelial Cells.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021 Sep;79(3):575-592. doi: 10.1007/s12013-021-01005-9. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021. PMID: 34085165 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion by sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) in acute lung injury: Role of S1P lyase.Adv Biol Regul. 2017 Jan;63:156-166. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2016.09.007. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Adv Biol Regul. 2017. PMID: 27720306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The sphingolipid degradation product trans-2-hexadecenal forms adducts with DNA.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Jul 20;424(1):18-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.06.012. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22727907 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase activity by electrospray ionization-liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry quantitation of (2E)-hexadecenal.Anal Biochem. 2011 Jan 1;408(1):12-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2010.08.026. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Anal Biochem. 2011. PMID: 20804717 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmalogens and fatty alcohols in rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata and Sjögren-Larsson syndrome.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2015 Jan;38(1):111-21. doi: 10.1007/s10545-014-9795-3. Epub 2014 Nov 29. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2015. PMID: 25432520 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasmalogen, a glycerophospholipid crucial for Streptococcus mutans acid tolerance and colonization.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Apr 17;90(4):e0150023. doi: 10.1128/aem.01500-23. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38456674 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Ether Lipids: Primordial Modulators of Cellular Signaling.Metabolites. 2021 Jan 8;11(1):41. doi: 10.3390/metabo11010041. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 33430006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Light-Triggered Carotenogenesis in Myxococcus xanthus: New Paradigms in Photosensory Signaling, Transduction and Gene Regulation.Microorganisms. 2021 May 15;9(5):1067. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9051067. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34063365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Don't Be Surprised When These Surprise You: Some Infrequently Studied Sphingoid Bases, Metabolites, and Factors That Should Be Kept in Mind During Sphingolipidomic Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 14;26(2):650. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020650. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasmalogens and Photooxidative Stress Signaling in Myxobacteria, and How it Unmasked CarF/TMEM189 as the Δ1'-Desaturase PEDS1 for Human Plasmalogen Biosynthesis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 May 11;10:884689. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.884689. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35646900 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aloulou A, Rahier R, Arhab Y, Noiriel A, Abousalham A, Phospholipases: An Overview, Methods Mol. Biol, 1835 (2018) 69–105. - PubMed
-
- Chap H, Forty five years with membrane phospholipids, phospholipases and lipid mediators: A historical perspective, Biochimie, 125 (2016) 234–249. - PubMed
-
- Eyster KM, The membrane and lipids as integral participants in signal transduction: lipid signal transduction for the non-lipid biochemist, Adv Physiol Educ, 31 (2007) 5–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

