Skeletal Stem Cells for Bone Development and Repair: Diversity Matters
- PMID: 32172443
- PMCID: PMC7255932
- DOI: 10.1007/s11914-020-00572-9
Skeletal Stem Cells for Bone Development and Repair: Diversity Matters
Abstract
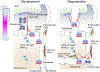
Purpose of review: Skeletal stem cells (SSCs) are considered to play important roles in bone development and repair. These cells have been historically defined by their in vitro potential for self-renewal and differentiation into "trilineage" cells; however, little is known about their in vivo identity. Here, we discuss recent progress on SSCs and how they potentially contribute to bone development and repair.
Recent findings: Bone is composed of diverse tissues, which include cartilage and its perichondrium, cortical bone and its periosteum, and bone marrow and its trabecular bone and stromal compartment. We are now at the initial stage of understanding the precise identity of SSCs in each bone tissue. The emerging concept is that functionally dedicated SSCs are encased by their own unique cellular and extracellular matrix microenvironment, and locally support its own compartment. Diverse groups of SSCs are likely to work in concert to achieve development and repair of the highly functional skeletal organ.
Keywords: Bone development; Bone regeneration; In vivo lineage-tracing experiments; Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs); Single-cell RNA-seq; Skeletal stem cells (SSCs).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Metcalf D On hematopoietic stem cell fate. Immunity. 2007;26(6): 669–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

