Regional Patterns and Association Between Obesity and Hypertension in Africa: Evidence From the H3Africa CHAIR Study
- PMID: 32172619
- PMCID: PMC7176339
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.14147
Regional Patterns and Association Between Obesity and Hypertension in Africa: Evidence From the H3Africa CHAIR Study
Abstract
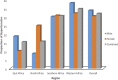
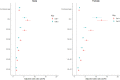
Hypertension and obesity are the most important modifiable risk factors for cardiovascular diseases, but their association is not well characterized in Africa. We investigated regional patterns and association of obesity with hypertension among 30 044 continental Africans. We harmonized data on hypertension (defined as previous diagnosis/use of antihypertensive drugs or blood pressure [BP]≥140/90 mmHg/BP≥130/80 mmHg) and obesity from 30 044 individuals in the Cardiovascular H3Africa Innovation Resource across 13 African countries. We analyzed data from population-based controls and the Entire Harmonized Dataset. Age-adjusted and crude proportions of hypertension were compared regionally, across sex, and between hypertension definitions. Logit generalized estimating equation was used to determine the independent association of obesity with hypertension (P value <5%). Participants were 56% women; with mean age 48.5±12.0 years. Crude proportions of hypertension (at BP≥140/90 mmHg) were 47.9% (95% CI, 47.4-48.5) for Entire Harmonized Dataset and 42.0% (41.1-42.7) for population-based controls and were significantly higher for the 130/80 mm Hg threshold at 59.3% (58.7-59.9) in population-based controls. The age-adjusted proportion of hypertension at BP≥140/90 mmHg was the highest among men (33.8% [32.1-35.6]), in western Africa (34.7% [33.3-36.2]), and in obese individuals (43.6%; 40.3-47.2). Obesity was independently associated with hypertension in population-based controls (adjusted odds ratio, 2.5 [2.3-2.7]) and odds of hypertension in obesity increased with increasing age from 2.0 (1.7-2.3) in younger age to 8.8 (7.4-10.3) in older age. Hypertension is common across multiple countries in Africa with 11.9% to 51.7% having BP≥140/90 mmHg and 39.5% to 69.4% with BP≥130/80 mmHg. Obese Africans were more than twice as likely to be hypertensive and the odds increased with increasing age.
Keywords: Africa; blood pressure; hypertension; obesity; risk factors.
Figures
References
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365:217–223. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)17741-1. - PubMed
-
- Van de Vijver S, Akinyi H, Oti S, Olajide A, Agyemang C, Aboderin I, Kyobutungi C. Status report on hypertension in Africa - consultative review for the 6th Session of the African Union Conference of Ministers of Health on NCDs. Pan Afr Med J. 2013;16:38. doi:10.11604/pamj.2013.16.38.3100. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Danaei G, Shibuya K, Adair-Rohani H, Amann M, Anderson HR, Andrews KG, Aryee M, et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2224–2260. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61766-8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO. Raised blood pressure. Global Health Observatory Data 2016. Available at: http://www.who.int/gho/ncd/risk_factors/blood_pressure_prevalence_text/en/. Accessed October 2017.
-
- Njelekela MA, Mpembeni R, Muhihi A, Mligiliche NL, Spiegelman D, Hertzmark E, Liu E, Finkelstein JL, Fawzi WW, Willett WC, et al. Gender-related differences in the prevalence of cardiovascular disease risk factors and their correlates in urban Tanzania. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2009;9:30. doi: 10.1186/1471-2261-9-30. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

