Nitric Oxide and Endothelial Dysfunction
- PMID: 32172815
- PMCID: PMC9015729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccc.2019.12.009
Nitric Oxide and Endothelial Dysfunction
Abstract
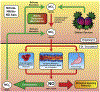
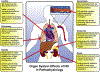
Nitric oxide is a strong vasodilatory and anti-inflammatory signaling molecule that plays diverse roles in maintaining vascular homeostasis. Nitric oxide produced by endothelial cells is a critical regulator of this balance, such that endothelial dysfunction is defined as a reduced capacity for nitric oxide production and decreased nitric oxide sensitivity. This ultimately results in an imbalance in vascular homeostasis leading to a prothrombotic, proinflammatory, and less compliant blood vessel wall. Endothelial dysfunction is central in numerous pathophysiologic processes. This article reviews mechanisms governing nitric oxide production and downstream effects, highlighting the role of nitric oxide signaling in organ system pathologies.
Keywords: Endothelial dysfunction; Nitric oxide; Nitric oxide synthase.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Sturtzel C Endothelial cells. In: Sattler S, Kennedy-Lydon T, editors. The Immunology of Cardiovascular Homeostasis and Pathology. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol. 1003. Cham: Springer; 2017.
-
- Incalza MA, D’Oria R, Natalicchio A, et al. Oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species in endothelial dysfunction associated with cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Vascul Pharmacol 2018;100(June 2017):1–19. - PubMed
-
- Tousoulis D, Kampoli A-M, Tentolouris Nikolaos Papageorgiou C, et al. The role of nitric oxide on endothelial function. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2012;10(1):4–18. - PubMed
-
- Gresele P, Momi S, Guglielmini G. Nitric oxide-enhancing or -releasing agents as antithrombotic drugs. Biochem Pharmacol 2019;166(June):300–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

