SPOT-Disorder2: Improved Protein Intrinsic Disorder Prediction by Ensembled Deep Learning
- PMID: 32173600
- PMCID: PMC7212484
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gpb.2019.01.004
SPOT-Disorder2: Improved Protein Intrinsic Disorder Prediction by Ensembled Deep Learning
Abstract
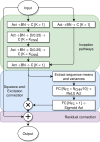
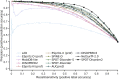
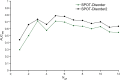
Intrinsically disordered or unstructured proteins (or regions in proteins) have been found to be important in a wide range of biological functions and implicated in many diseases. Due to the high cost and low efficiency of experimental determination of intrinsic disorder and the exponential increase of unannotated protein sequences, developing complementary computational prediction methods has been an active area of research for several decades. Here, we employed an ensemble of deep Squeeze-and-Excitation residual inception and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks for predicting protein intrinsic disorder with input from evolutionary information and predicted one-dimensional structural properties. The method, called SPOT-Disorder2, offers substantial and consistent improvement not only over our previous technique based on LSTM networks alone, but also over other state-of-the-art techniques in three independent tests with different ratios of disordered to ordered amino acid residues, and for sequences with either rich or limited evolutionary information. More importantly, semi-disordered regions predicted in SPOT-Disorder2 are more accurate in identifying molecular recognition features (MoRFs) than methods directly designed for MoRFs prediction. SPOT-Disorder2 is available as a web server and as a standalone program at https://sparks-lab.org/server/spot-disorder2/.
Keywords: Deep learning; Intrinsic disorder; Machine learning; Molecular recognition feature; Protein structure.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identifying molecular recognition features in intrinsically disordered regions of proteins by transfer learning.Bioinformatics. 2020 Feb 15;36(4):1107-1113. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz691. Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 31504193
-
Accurate Single-Sequence Prediction of Protein Intrinsic Disorder by an Ensemble of Deep Recurrent and Convolutional Architectures.J Chem Inf Model. 2018 Nov 26;58(11):2369-2376. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00636. Epub 2018 Nov 13. J Chem Inf Model. 2018. PMID: 30395465
-
Identifying short disorder-to-order binding regions in disordered proteins with a deep convolutional neural network method.J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2019 Feb;17(1):1950004. doi: 10.1142/S0219720019500045. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 30866736
-
A comprehensive review and comparison of existing computational methods for intrinsically disordered protein and region prediction.Brief Bioinform. 2019 Jan 18;20(1):330-346. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx126. Brief Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 30657889 Review.
-
The contribution of intrinsic disorder prediction to the elucidation of protein function.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013 Jun;23(3):467-72. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2013.02.001. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013. PMID: 23466039 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein Function Analysis through Machine Learning.Biomolecules. 2022 Sep 6;12(9):1246. doi: 10.3390/biom12091246. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36139085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biophysical and Integrative Characterization of Protein Intrinsic Disorder as a Prime Target for Drug Discovery.Biomolecules. 2023 Mar 14;13(3):530. doi: 10.3390/biom13030530. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36979465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of protein-protein interaction sites in intrinsically disordered proteins.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Sep 30;9:985022. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.985022. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36250006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PentUnFOLD algorithm as a tool to distinguish the dark and the light sides of the structural instability of proteins.Amino Acids. 2022 Aug;54(8):1155-1171. doi: 10.1007/s00726-022-03153-5. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Amino Acids. 2022. PMID: 35294674 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Insights into the Intrinsically Disordered GPCR C-Terminal Region, Major Actor in Arrestin-GPCR Interaction.Biomolecules. 2022 Apr 21;12(5):617. doi: 10.3390/biom12050617. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35625550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Uversky V.N., Oldfield C.J., Dunker A.K. Showing your ID: intrinsic disorder as an ID for recognition, regulation and cell signaling. J Mol Recognit. 2005;18:343–384. - PubMed
-
- Wright P.E., Dyson H.J. Intrinsically unstructured proteins: re-assessing the protein structure-function paradigm. J Mol Biol. 1999;293:321–331. - PubMed
-
- Uversky V.N. Functions of short lifetime biological structures at large: the case of intrinsically disordered proteins. Brief Funct Genomics. 2018 Ely023. - PubMed
-
- Dyson H.J., Wright P.E. Intrinsically unstructured proteins and their functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:197–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

