Protective effects of new aryl sulfone derivatives against radiation-induced hematopoietic injury
- PMID: 32173735
- PMCID: PMC7299261
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rraa009
Protective effects of new aryl sulfone derivatives against radiation-induced hematopoietic injury
Abstract
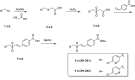
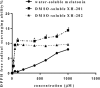
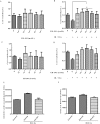
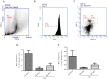
The hematopoietic system is sensitive to radiation. In this research, new aryl sulfone derivatives (XH-201 and XH-202) containing a nitrogen heterocycle were designed and synthesized and their radio-protective efficacies with regard to the hematopoietic system were evaluated. XH-201 administration significantly increased the survival rate of mice after 8.0 Gy total body irradiation (TBI). The results showed that XH-201 treatment not only increased the white blood cells, platelets counts and the percentage of hematopoietic progenitor cells and hematopoietic stem cells in mice exposed to 4.0 Gy TBI but also decreased DNA damage, as determined by flow cytometric analysis of histone H2AX phosphorylation. In addition, our data demonstrated that XH-201 decreased the mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in hematopoietic cells. Overall, these data suggest that XH-201 is beneficial for the protection of the hemoatopoietic system against radiation-induced injuries.
Keywords: aryl sulfone derivatives; hematopoietic cells; radioprotection.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japanese Radiation Research Society and Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology.
Figures


References
-
- Kamran MZ, Ranjan AN, Kaur S et al. Radioprotective agents: Strategies and translational advances. Med Res Rev 2016;36:461–93. - PubMed
-
- Johnke RM, Sattler JA, Allison RR. Radioprotective agents for radiation therapy: Future trends. Future Oncol 2014;10:2345–57. - PubMed
-
- Patyar RR, Patyar S. Role of drugs in the prevention and amelioration of radiation induced toxic effects. Eur J Pharmacol 2018;819:207–16. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

