False-Negative Results of Real-Time Reverse-Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2: Role of Deep-Learning-Based CT Diagnosis and Insights from Two Cases
- PMID: 32174053
- PMCID: PMC7082661
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0146
False-Negative Results of Real-Time Reverse-Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2: Role of Deep-Learning-Based CT Diagnosis and Insights from Two Cases
Abstract
The epidemic of 2019 novel coronavirus, later named as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is still gradually spreading worldwide. The nucleic acid test or genetic sequencing serves as the gold standard method for confirmation of infection, yet several recent studies have reported false-negative results of real-time reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR). Here, we report two representative false-negative cases and discuss the supplementary role of clinical data with rRT-PCR, including laboratory examination results and computed tomography features. Coinfection with SARS-COV-2 and other viruses has been discussed as well.
Keywords: COVID-19; Computed tomography; False-negative results; Laboratory examination; SARS-COV-2; rRT-PCR.
Copyright © 2020 The Korean Society of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
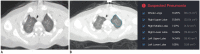
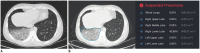
Comment in
-
A Patient with COVID-19 Presenting a False-Negative Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction Result.Korean J Radiol. 2020 May;21(5):623-624. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0195. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Korean J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32207257 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Rapidly Progressive COVID-19 Pneumonia: What Radiologists Should Do.Korean J Radiol. 2020 Jun;21(6):773-776. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0364. Korean J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32410416 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
COVID-19 Carrier or Pneumonia: Positive Real-Time Reverse-Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction but Negative or Positive Chest CT Results.Korean J Radiol. 2020 Jul;21(7):925-928. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0360. Korean J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32524793 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A COVID-19 patient with seven consecutive false-negative rRT-PCR results from sputum specimens.Intern Emerg Med. 2020 Aug;15(5):871-874. doi: 10.1007/s11739-020-02423-y. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Intern Emerg Med. 2020. PMID: 32617907 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Gorbalenya AE, Baker SC, Baric RS, de Groot RJ, Drosten C, Gulyaeva AA, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: the species and its viruses - a statement of the Coronavirus Study Group. bioRxiv; 2020. [Accessed February 11,2020]. Available at: - DOI
-
- National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Diagnosis and treatment protocols of pneumonia caused by a novel coronavirus (trial version 5) Beijing: National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China; 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

