Lived Experiences of Fragile X Syndrome Caregivers: A Scoping Review of Qualitative Studies
- PMID: 32174884
- PMCID: PMC7056838
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00128
Lived Experiences of Fragile X Syndrome Caregivers: A Scoping Review of Qualitative Studies
Abstract
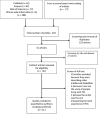
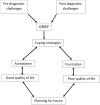
Fragile X Syndrome (FXS) is the most common x-linked monogenic cause of Intellectual Disability (ID) and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Taking care of children with ID is challenging and overwhelming due to the multiple facets of caregiving. This scoping review aimed at summarizing the qualitative literature on the experiences of families living with FXS, identify key themes and determine the gaps in the extant literature. We conducted a literature search in May 2019 using four databases; PubMed, Web of Science, African-Wide-Information, and Scopus. The keywords used in our search strategy were associated with caregivers, lived experiences, FXS, and qualitative research. All English language articles with full-text reporting were included. Studies associated with other neurodevelopmental conditions and quantitative studies were excluded. We identified 12 out of 203 articles that described the lived experiences of families with FXS. Most articles originated from the United States of America and mothers were the main caregivers. We summarized our findings into four major themes which are; grief experiences, challenges of living with FXS, coping mechanisms and the need to plan for future outcomes. This scoping review highlights the scarcity of qualitative FXS literature in the African population and frustrations endured by families with FXS due to the low knowledge of FXS by healthcare workers. More research is needed to evaluate the impact of living with FXS in males and fathers.
Keywords: care givers; fragile X syndrome; lived experience; qualitative research; scoping review.
Copyright © 2020 Kamga, De Vries, Nguefack, Munung and Wonkam.
Figures
References
-
- Hagerman RJ, Hendren RL. Treatments of Neurodevelopmental Disorders: Targeting Neurobiological Mechanisms. New York, NY: Oxford University Press (2014). p. 376 10.1093/med/9780199937806.001.0001 - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources