Integration Analysis of m6A-SNPs and eQTLs Associated With Sepsis Reveals Platelet Degranulation and Staphylococcus aureus Infection are Mediated by m6A mRNA Methylation
- PMID: 32174955
- PMCID: PMC7054457
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00007
Integration Analysis of m6A-SNPs and eQTLs Associated With Sepsis Reveals Platelet Degranulation and Staphylococcus aureus Infection are Mediated by m6A mRNA Methylation
Abstract
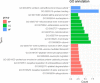
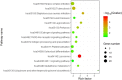
Sepsis is a major threat with high mortality rate for critically ill patients. Response to pathogen infection by the host immune system is a key biological process involved in the onset and development of sepsis. Heterogeneous host genome variation, especially single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), has long been suggested to contribute to differences in disease progression. However, the function of SNPs located in non-coding regions remains to be elucidated. Recently, m6A mRNA modification levels were revealed to differ at SNPs. As m6A is a crucial regulator of gene expression, these SNPs might control genes by changing the m6A level on mRNA. To investigate the potential role of m6A SNPs in sepsis, we integrated m6A-SNP and expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) data. Analysis revealed 15,720 m6A-cis-eQTLs and 381 m6A-trans-eQTLs associated with sepsis. We identified 1321 genes as locations of m6A-cis-eQTLs. These were enriched in platelet degranulation and Staphylococcus aureus infection pathways, which are vital for the pathophysiological process of sepsis. We conclude that m6A modification of mRNA plays a very important role in sepsis, with m6A-cis-eQTLs potentially having the most effect on individual variation in sepsis progression.
Keywords: M6A; Staphylococcus aureus; eQTL; methylation; sepsis.
Copyright © 2020 Sun, Dai, Tan, Liu and Li.
Figures

References
-
- Alvarez-Estrada A., Rodriguez-Ferri E. F., Martinez-Martinez S., Alvarez B., Fernandez-Caballero T., Dominguez J., et al. (2019). TLR2, Siglec-3 and CD163 expressions on porcine peripheral blood monocytes are increased during sepsis caused by Haemophilus parasuis . Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 64, 31–39. 10.1016/j.cimid.2019.02.001 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

